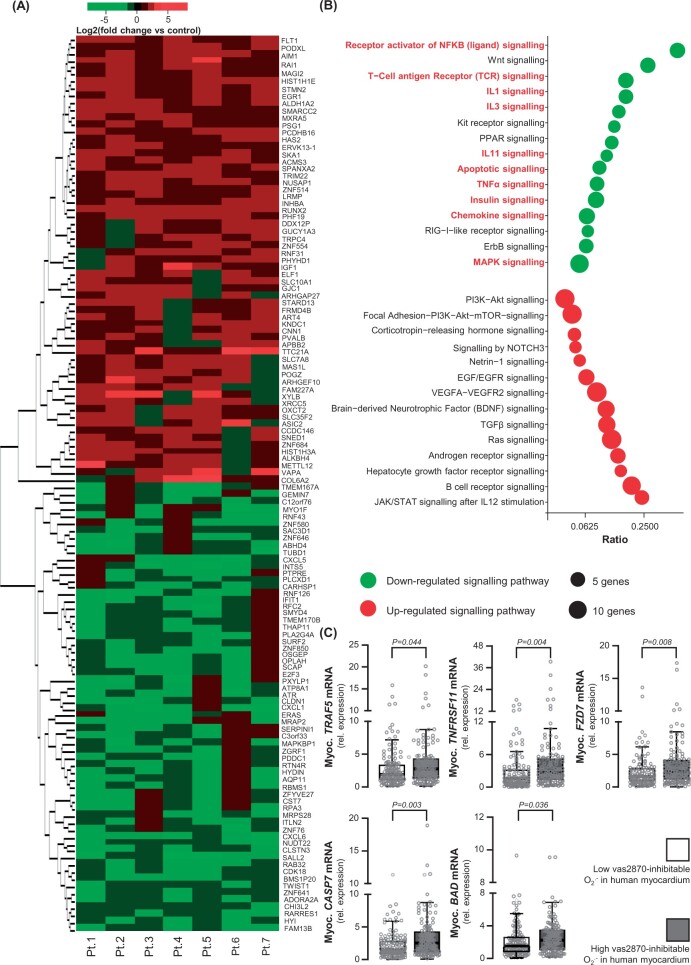
Figure 6.
Canagliflozin has a global anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effect on human cardiomyocytes. In this experiment, human cardiomyocytes were cultured in high-glucose medium (25 mM) for 72 h and then treated with canagliflozin (10 μM) or DMSO for 24 h. Heat map of 127 down- or up-regulated genes by canagliflozin (fold change >1.5 or `−1.5, P < 0.05) in canagliflozin-treated human cardiomyocytes from n = 7 patients (A). NFkB, Wnt, IL1, IL3, TNFα, chemokine, MAPK pathways, and apoptotic pathways (highlighted by red font) were down-regulated by canagliflozin (more than 50% of pathway genes down-regulated by canagliflozin, B). TNFRSF11, TRAF5, FZD7, CASP7, and BAD were the most down-regulated individual genes upon canagliflozin treatment, implicated in NFkB, TNFα, and apoptosis pathways. The mRNA expression of these genes was positively correlated with myocardial NADPH oxidase activity (i.e. high Vas2870-inhibitable signal) in 240 atrial biopsies from Study 1 (C). Data are presented as median [25th–75th percentile]. P-values are calculated by Mann–Whitney U-test for high (above median) vs. low (below median).