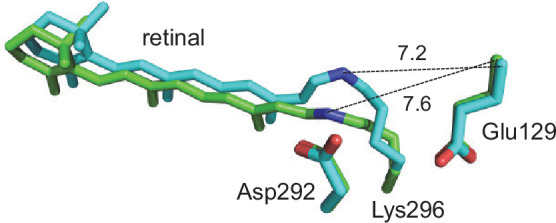
Figure 5. Channel space in GtACR1.
(a) Channel space and side-chain orientations in the wild-type (gray sticks, PDB code 6EDQ; Li et al., 2019) and D234N (green sticks, a representative MD-generated conformation) GtACR1s. The yellow mesh indicates the channel space in the wild-type GtACR1 analyzed using the CAVER program (Chovancova et al., 2012). Note that the channel space is consistent with that reported by Li et al., 2019. Channel space and side-chain orientations in the representative MD-generated structures of (b) wild-type and (c) D234N GtACR1s. Chovancova et al., 2012 The red arrow indicates the decrease in the channel space (radius) owing to the approach of Glu68. (d) Channel radii along the channel in wild-type (dotted black line) and D234N (solid red line) GtACR1s. The red open circle indicates the constriction created by reoriented Glu68 in D234N GtACR1.
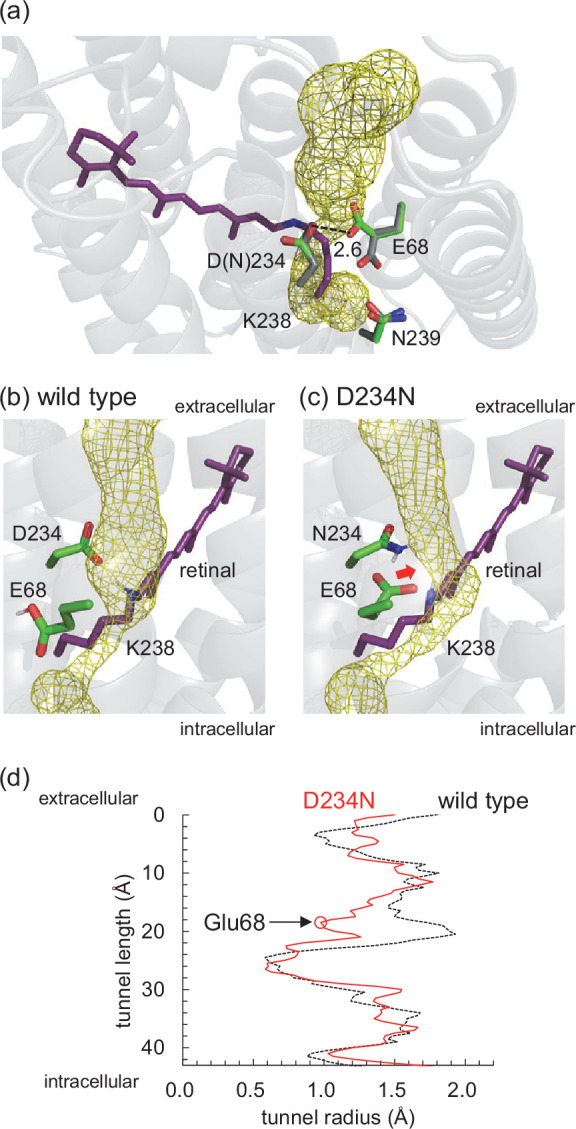
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Retinal Schiff base, Glu129 (Glu68 in GtACR1), and Asp292 (Asp234 in GtACR1) in the structures of the ground state (green sticks, PDB code 7C86; Oda et al., 2021) and 4 ms after light irradiation (cyan sticks, PDB code 7E6X; Oda et al., 2021) of cation channelrhodopsin C1C2.