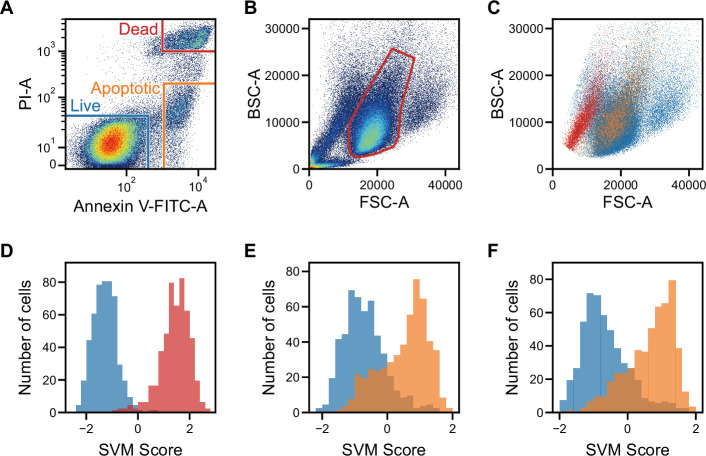
Figure 3. Classification of live, dead, and apoptotic iPSCs with iSGC.
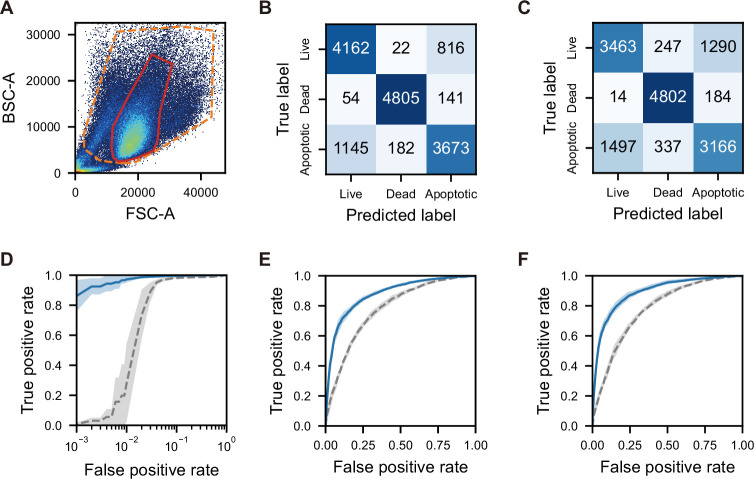
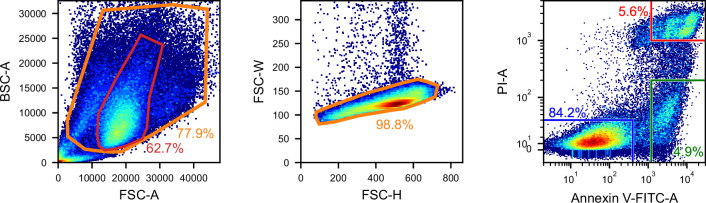
(A). Scatter plot of PI and Annexin V for iPSCs. The population within the blue, red, and orange regions were labeled as live, dead, and apoptotic cells, respectively. (B). Scatter plot of FSC and BSC for iPSCs without exclusion of debris and doublets. (C). Scatter plot of FSC and BSC for each labeled iPSC populations. The blue, red, and orange dots each correspond to live, dead, and apoptotic cells, respectively. All populations, which are previously shown in (B), are gated prior to labeling for removing debris and doublets (Figure 3—figure supplement 1A and Figure 3—figure supplement 2). In the plot, the live and dead populations have distinct separation, but the live and apoptotic populations overlap. (D–F) SVM score histograms for the iSGC-based classification of dead cells from live cells (D), apoptotic cells from live cells (E), and apoptotic cells from live cells within the red region in the scatter plot (B, F). The colors correspond to the labels in (A). All histograms are the best result of 10 times random sampling. The AUCs for each classification were 0.999 (D), 0.885 (E), and 0.904 (F). The mean and standard deviation of AUCs for the 10 trials in each condition were 0.998±0.002, 0.877±0.007, and 0.891±0.012, respectively (Figure 3—figure supplement 1, D, E, and F). BSC, back scatter; FSC, forward scatter; iPSC, induced pluripotent stem cell; iSGC, in silico-labeled ghost cytometry; PI, propidium iodide; SVM, support vector machine.