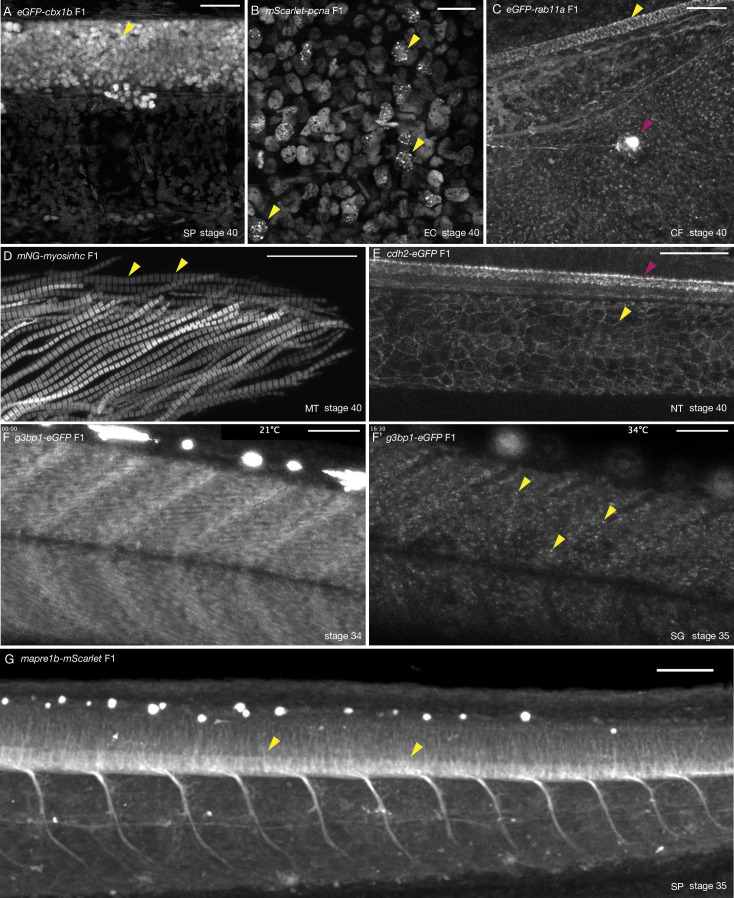
Figure 2. Tissue- and organelle-specific expression of seven CRISPR/Cas9 knock-in (KI) lines in medaka.
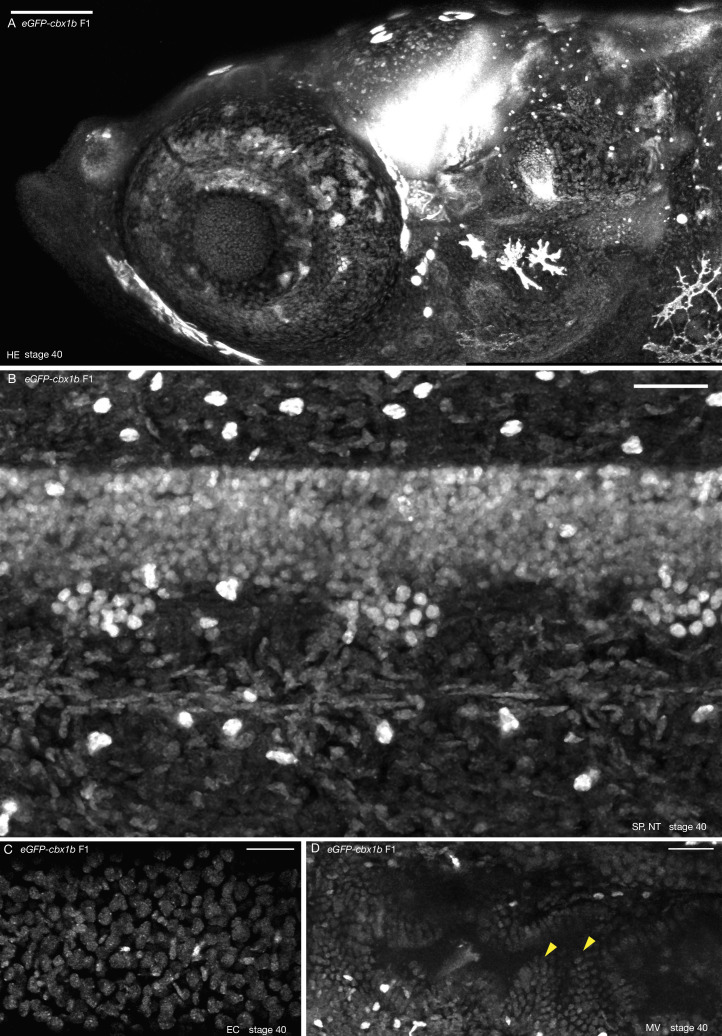
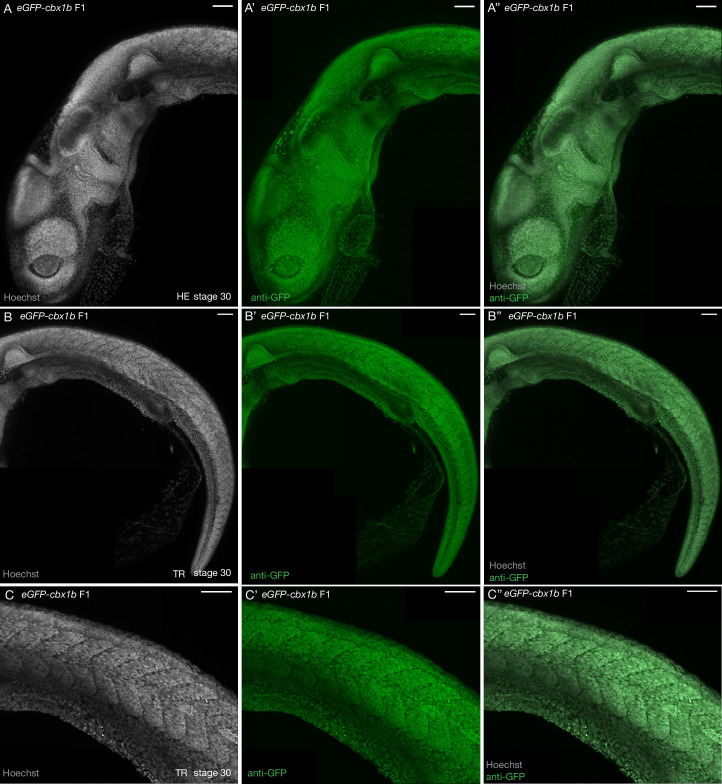
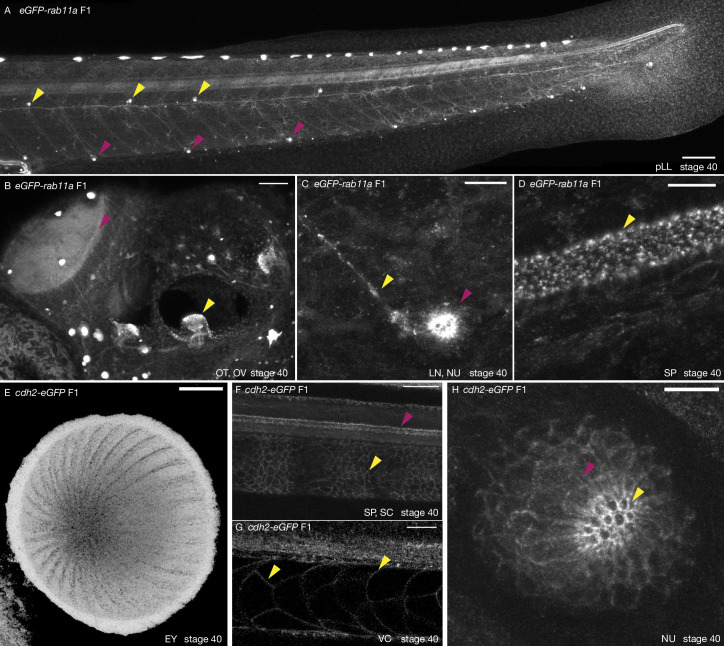
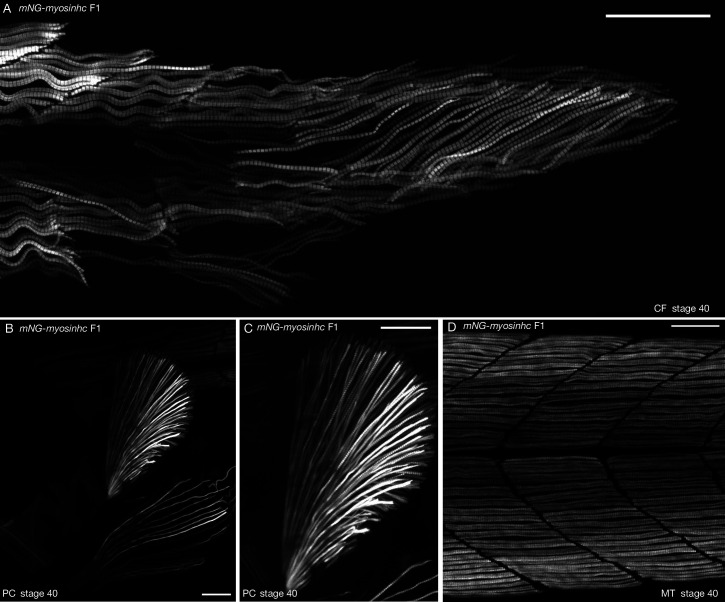
(A) eGFP-cbx1b F1 stage 40 medaka embryo. eGFP-Cbx1b labels all nuclei. Nuclei in the spinal cord of medaka are highlighted (yellow arrowhead). n > 10 embryos. SP = spinal cord. Scale bar = 30 µm. (B) mScarlet-pcna F1 stage 40 medaka embryo. mScarlet-Pcna is localized in the nuclei of cycling cells. mScarlet-Pcna is visible in skin epithelial cell nuclei located in the mid-trunk region of a medaka embryo. The localization of Pcna as speckles within the nucleus indicates cells in S phase of the cell cycle (yellow arrowheads). n = 10 embryos. EC = epithelial cells. Scale bar = 20 µm. (C) eGFP-rab11a F1 stage 40 medaka embryo. Expression of the membrane trafficking marker eGFP-Rab11a is evident in the caudal fin region. eGFP-Rab11a is strongly expressed in the spinal cord (yellow arrowhead) and lateral line neuromasts (magenta arrowhead). n = 6 embryos. CF = caudal fin. Scale bar = 30 µm. (D) mNG-myosinhc F1 stage 40 medaka embryo. mNG-Myosinhc is expressed solely in muscle cells. Myofibrils containing chains of individual sarcomere can be seen (mNG-Myosinhc labels the Myosin A band inside each sarcomere, yellow arrowheads). n > 10 embryos. MT = myotome. Scale bar = 30 µm. (E) cdh2-eGFP F1 stage 40 medaka embryo. Cdh2-eGFP is localized at cell membranes in several tissues, including the spinal cord (magenta arrowhead) and the notochord (yellow arrowhead). n = 5 embryos. NT = notochord. Scale bar = 50 µm. (F–F’) g3bp1-eGFP F1 stage 34–35 medaka embryo. Time-lapse imaging of G3bp1-eGFP dynamics under normal and stress conditions. (F) G3bp1-eGFP localizes to the cytoplasm under physiological conditions. (F’) Under stress conditions (temperature shock), G3bp1-eGFP localizes to stress granules (yellow arrowheads). Time in hours. n = 8 embryos. SG = stress granules. Scale bar = 50 µm. (G) mapre1b-mScarlet F1 stage 35 medaka embryo. Mapre1-mScarlet is expressed in a number of tissues and cell types including epithelial cells, muscle cells, the notochord, neuromasts and is highly expressed in the spinal cord. n = 5 embryos. SP = spinal cord. Scale bar = 50 µm.