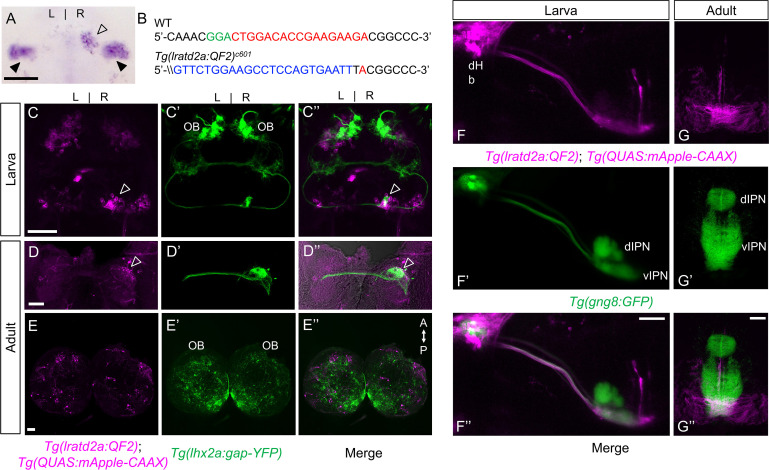
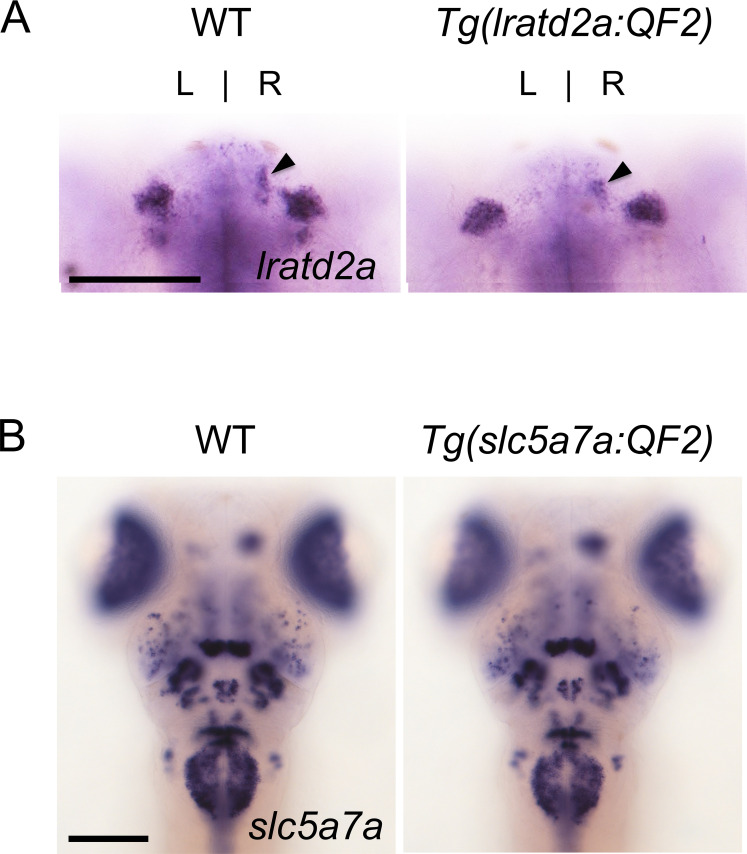
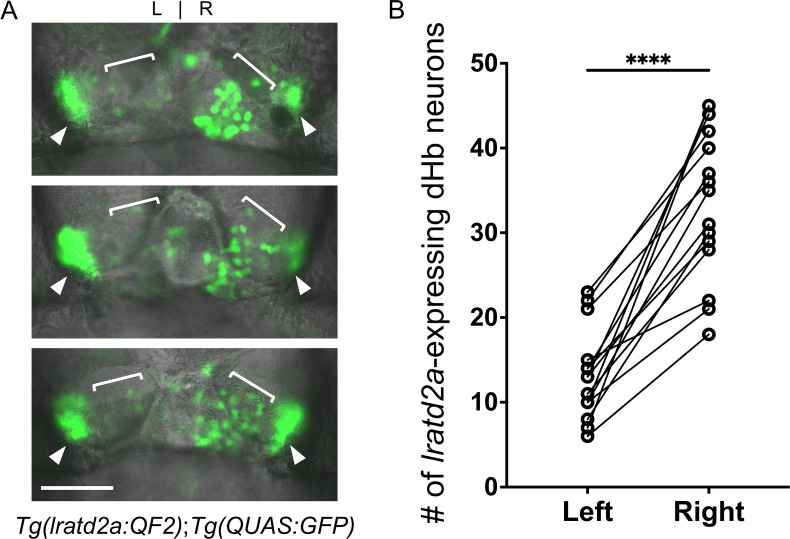
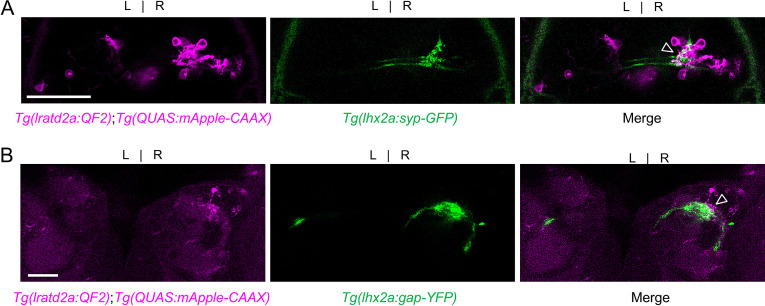
Figure 1. lratd2a-expressing neurons in the right dHb connect asymmetric pathway from the olfactory bulb to ventral IPN.
(A) Pattern of lratd2a expression at 5 days post fertilization (dpf), open arrowhead indicates right dHb and black arrowheads the bilateral vHb. (B) Sequences of WT (top) and transgenic fish (bottom) with QF2 integrated within the first exon of the lratd2a gene. PAM sequences are green, the sgRNA-binding site red and donor DNA blue. Confocal dorsal views of Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(QUAS:mApple-CAAX) and Tg(lhx2a:gap-YFP) labeling in a (C-C’’) 5 dpf larva and in transverse sections of the adult brain at 3 months post-fertilization (mpf) at the level of the (D-D’’) dHb and (E-E’’) olfactory bulb. Axons of lhx2a olfactory mitral cells (open arrowheads, C and D) terminate at lratd2a dHb neurons. (F-F’’) Lateral view of Tg(lratd2a:QF2), Tg(QUAS:mApple-CAAX), Tg(gng8:GFP) larva at 6 dpf with mApple-labeled dHb terminals at the ventral interpeduncular nucleus (vIPN). Dorsal habenular nuclei (dHb), dorsal interpeduncular nucleus (dIPN). (G-G’’) Axonal endings of lratd2a dHb neurons are restricted to the ventralmost region of the vIPN in transverse section of 2.5 mpf adult brain. Scale bar, 50 μm. A-P, anterior to posterior; L-R, left-right; OB, olfactory bulb.