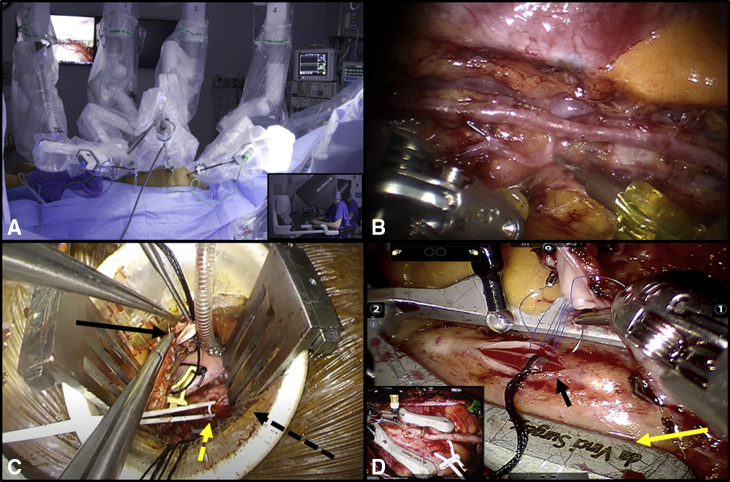
Figure 2.
A, This picture shows the 3 ports in the second, fourth, and sixth intercostal spaces with the robotic arms inserted into the ports. The inset shows the surgeon working at the console. B, The 3-dimensional view offered by the robotic platform enhances the visualization of the left internal thoracic artery (LITA) that is skeletonized. C, In robot-assisted coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), a small thoracotomy (3-4 cm) is performed in the fourth intercostal space along the midclavicular line (black hatched arrow). Black arrow shows the LITA and the yellow arrow shows the left anterior descending artery (LAD) that is proximally snared with a silastic loop while the surgeon performs an off-pump LITA-to-LAD anastomosis using a suction stabilizer. D, LITA to LAD anastomosis (black arrow) performed off-pump using the robotic surgical instruments and a 7-0 polypropylene suture facilitated by a robotic stabilizer (yellow arrow) inserted into the thorax through an additional port in totally endoscopic-CABG. The inset shows a completed anastomosis.