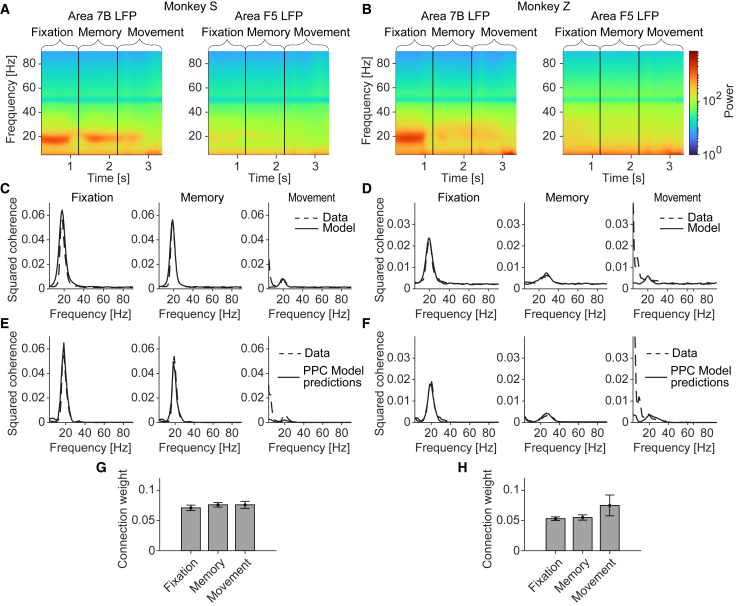
Figure 4.
7B-F5 coherence is predicted by 7B power
(A and B) Power spectra during different behavioral periods.
(C and D) 7B-F5 LFP coherence and the SSM model fits. Connectivity fits are shown in (G) and (H).
(E and F) SSM model predictions including estimates for the source-projection coherence based on the spike-LFP PPC within area 7B and using the coupling weights w of the model in (C) and (D).
(G and H) Coupling weights w for the different model fits in (C) and (D). Weights did not significantly differ between periods.
Significance of the coupling weights in (G) and (H) was estimated using Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Note that in (E) and (F), the model underestimates the low-frequency coherence in the movement period. The reason is that we modeled 7B-F5 coherence based only on the spike-field locking in 7B and ignored the locking in F5, which shows strong low-frequency phase locking and power. All error bars denote SEMs.