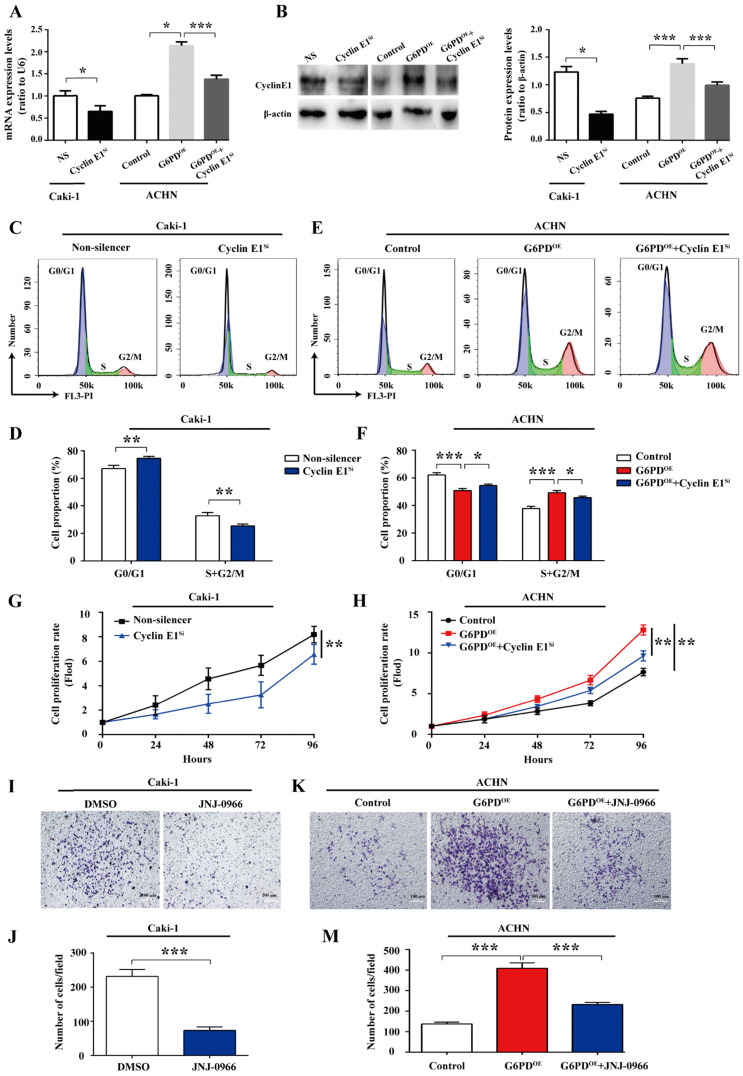
Figure 6.
Cyclin E1 and MMP9 are involved in the G6PD-mediated ccRCC cells proliferation and migration. (A-B) The expression of Cyclin E1 at the mRNA and protein level in Caki-1, ACHN-G6PDOE and relevant control cells was analyzed by using real-time RT-PCR (A) and Western blot assay (B), respectively at 48 h after Cyclin E1 siRNA transfection. β-actin was used as a protein loading control. Representative cropped gels and blots of the Western blot analysis were shown (B). (C-F) Cyclin E1 siRNA transfected Caki-1, ACHN-G6PDOE and relevant control cells were subjected to cell cycle distribution analysis by PI staining and flow cytometry assay. (G-H) Cell proliferation abilities of Caki-1-Cyclin E1si, ACHN-G6PDOE-Cyclin E1si and relevant control cell lines were assessed by MTS assay at different time points. (I-M) Caki-1, ACHN-G6PDOE cells following treatment with the MMP9 inhibitor JNJ-0966 (10 μM, 24 h) and relevant control cells were subjected to Transwell assays. Representative images (I, K) and quantification analyses (J, M) are shown. All assays were done in at least triplicate. Bars represent the means ± SD. *p <0.05, **p <0.01, ***p <0.001 vs. relevant control (Mixed ANOVA for G-H, unpaired Student's t-test for others).