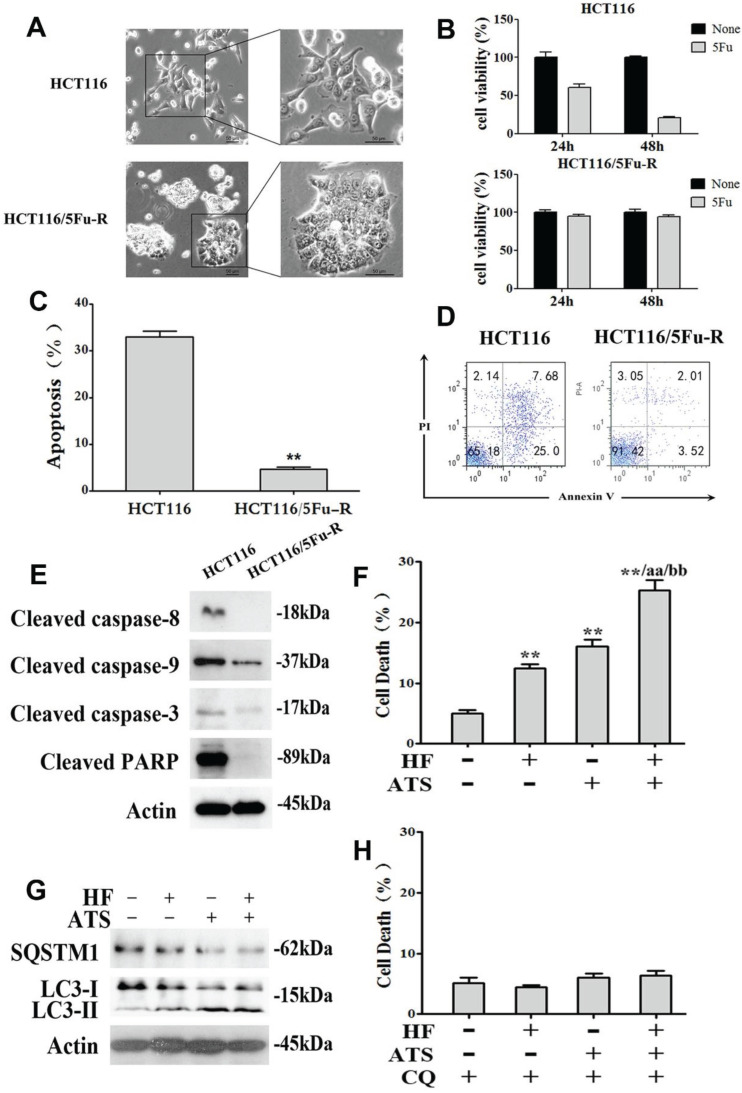
Figure 5.
HF-ATS induces autophagic death in 5Fu resistant HCT116 cells. (A) Morphologic analysis comparing parental and 5Fu resistant HCT116 cells. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) Cell viability between parental and 5Fu resistant HCT116 cells by MTT assay, which were exposed to 100 mM 5Fu for 24 h and 48 h. (C, D) 5Fu resistant HCT116 cells escape apoptosis. In C, apoptosis was quantified with flow cytometry. In D, flow cytometry analyses of apoptosis in parental and 5Fu resistant HCT116 cells, both exposed to 100 mM 5Fu for 24 h. (E) Expression of cleaved caspase-8, caspase-9, caspase-3 and PARP regulated by 100 mM 5Fu in 5Fu resistant HCT116 cells. (F) Cell death was quantified by combination of HF (10 nM) and ATS (160 μM) for 24 h in 5Fu resistant HCT116 cells. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, compared with control group. a P < 0.05, aa P < 0.01, compared with HF. b P < 0.05, bb P < 0.01, compared with ATS. (G) Expression of cleaved SQSTM1 and LC3-II regulated by combination of HF (10 nM) and ATS (160 μM) for 24 h in 5Fu resistant HCT116 cells. (H) Cell death was quantified by combination of HF (10 nM) and ATS (160 μM) for 24 h in 5Fu resistant HCT116 cells co-treated with autophagic inhibitor CQ.