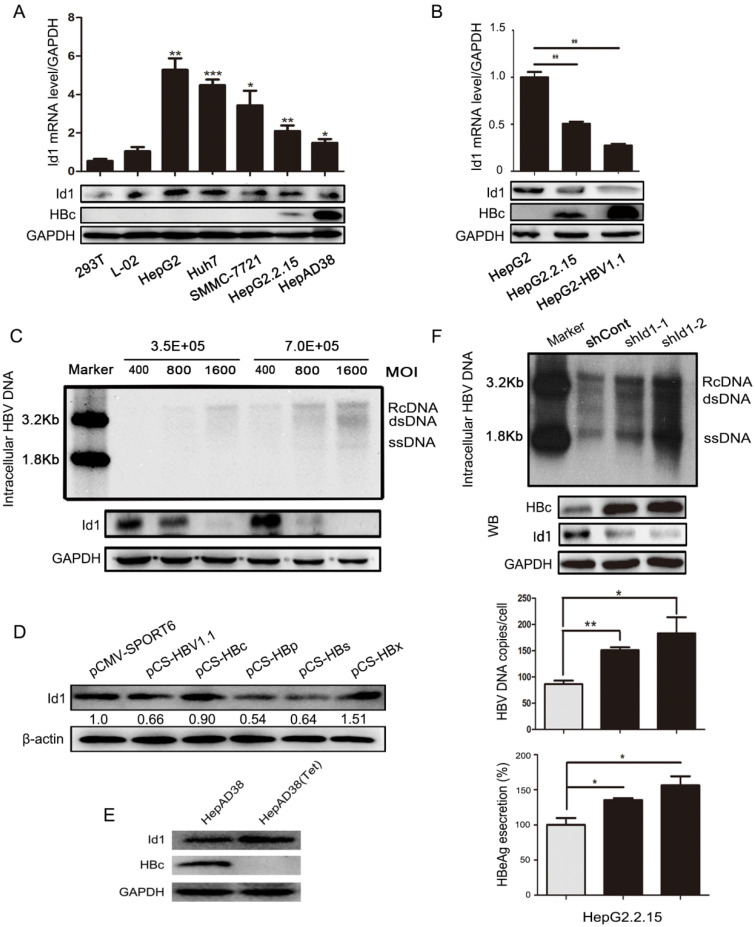
Figure 1.
The comparison of Id1 expression in HBV or non-HBV context, and Id1 knockdown promoted HBV replication. (A) The Id1 mRNA (top layer) and protein (bottom layer) levels in 293T, L02,HepG2, Huh7,SMMC-7721,HepG2.2.15 and HepAD38 cells were analyzed by qPCR and western blotting with GAPDH used as the control gene. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. n = 5. (B) The Id1 mRNA (top layer) and protein (bottom layer) levels in HepG2, HepG2.2.15 and HepG2-HBV1.1, which was transiently transfected with plasmid HBV1.1, were detected by qPCR and western blotting with GAPDH used as the control gene. **P < 0.01. n = 5. (C) 3.5×105 or 7×105 Cells/35mm dish were infected with 400, 800 and 1600 HBV particles /cell. Then the cells were lysed and extracted for HBV DNA, which followed with southern blotting (top panel). Id1 protein levels of each cell dish infected with different virus titer of HBV were detected by western blotting (bottom panel). (D) Four plamids respectively expressing HBc/p/s/x proteins and HBV1.1 were transfected into HepG2 cells to verify the effect of HBV on Id1. (E) The HBc and Id1 protein level in HepAD38 cells with tetracycline-inhibiting HBV transcription was detected by western blotting with GAPDH used as the control gene. (F) HepG2.2.15 cells transfected with shRNA plasmids targeting Id1 or shCont vector as control group were harvested 72h, and intracellular HBV DNA was extracted and precipitated by isopropanol after viral infection. HBV DNA was determined by southern blotting and qPCR. Southern blotting analysis: Maker 1.8kb and 3.2kb; RcDNA, HBV relax circle DNA; dsDNA, double-stranded DNA; ssDNA, single-stranded DNA. The qPCR data were expressed as the number of HBV DNA copies per cell. HBc and Id1 protein was determined by Western blotting. Meanwhile, GAPDH was used as a loading control. Expression of HBeAg in the supernatant of cell culture media were detected using ELISA 3 days after transfection. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. n = 5.