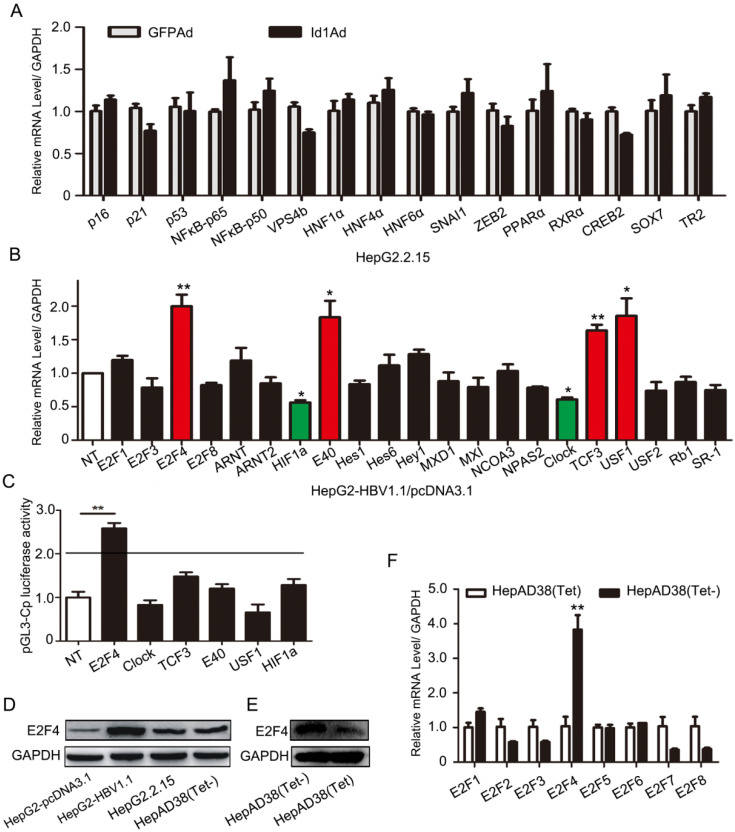
Figure 3.
Regulation of HBV transcription was involved in E2F4. (A) Genes including P16, P21, p53, NFԟB-p65, NFԟB-p50, VPS4b, HNF1ɑ, HNF4ɑ, HNF6ɑ, SNAI1, ZEB2, PPARɑ, RXRɑ, CREB2, SOX7, and TR2, which have been reported to play important roles in transcription or replication of HBV, were screened. qPCR analysis of gene expression of various transcription factors related to HBV replication in HepG2.2.15 after being infected with Id1Ad. n = 3. (B) The qPCR analysis was subjected to screen gene expression of various HLH transcription factors possibly related to Id1 in HepG2 transfected with HBV1.1 plasmid. GAPDH expression was used as internal control. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. n = 5. (C) Effects of a series of HLH transcription factors (including E2F4, CLOCK, TCF3, E40, USF1, HIF1ɑ ) overexpression on HBV Cp promoters were screened. Luciferase reporter vectors pGL3-Cp were cotransfected with overexpression plasmid into HepG2 cells. The cells were lysed and luciferase activity was determined at 48h after transfection. Meanwhile, the plasmid pRL-TK was used for normalizing the transfection efficiency. **P <0.01. n = 5. (D) The comparison of E2F4 protein level among HepG2, HepG2-HBV1.1, HepG2.2.15 and HepAD38 (without tetracycline). (E) The E2F4 protein level in HepAD38 cells with tetracycline-inhibiting HBV transcription was detected by western blotting with GAPDH used as the control gene. (F) The qPCR analysis was subjected to screen gene expression of various E2F transcription factor in HepAD38 cells with tetracycline-inhibiting HBV transcription. **P < 0.01. n = 5.