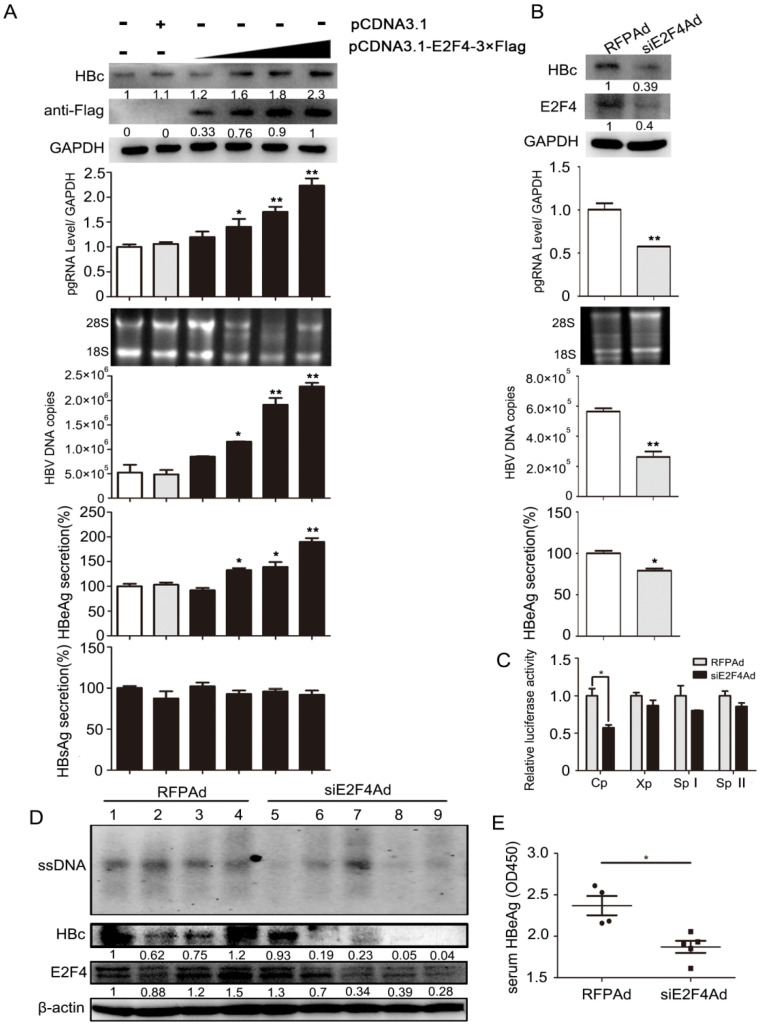
Figure 4.
Regulation of HBV transcription in vivo and in vitro was positively mediated by E2F4. (A) HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected with an empty vector (pcDNA3.1) or increasing amounts of pcDNA3.1-E2F4-3×Flag expressing plasmids. After 3 days, expression of the Flag-tagged E2F4 and HBc proteins were analyzed by Western blotting. HBV DNA and pgRNA levels in cytoplasmic fractions were measured by qPCR, and expression of HBeAg and HBsAg in the supernatant of cell culture media were detected using ELISA. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. n = 5. (B) HepG2.2.15 cells were infected with RFPAd or siE2F4Ad. After 3 days, E2F4 and HBc proteins, HBV DNA and pgRNA, and HBeAg were detected. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. n = 5. (C) Effect of E2F4 on activity of HBV pGL3-Cp/Xp/SpI /SpII promoters were measured via dual luciferase reporter assay. *P < 0.05. n = 5. (D) The mice were randomly allotted to two groups of five individuals per group. Moderate siE2F4Ad or RFPAd were dissolved in 0.3 mL 0.9% normal saline and injected through the tail vein. The mice were sacrificed 20 days after injection and the liver tissue. Intracellular HBV DNA extracted from 10 mg liver tissue was analysed by Southern blotting (top panel). The expression of E2F4 and HBc in liver tissue lysates was tested by western blotting. β-actin protein level was used as an internal control. (E) The relative levels of HBeAg in serum samples were subjected by ELISA kits; **P < 0.01. n = 5.