Figure 2. PTEN mutations in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and congenital hydrocephalus (CH).
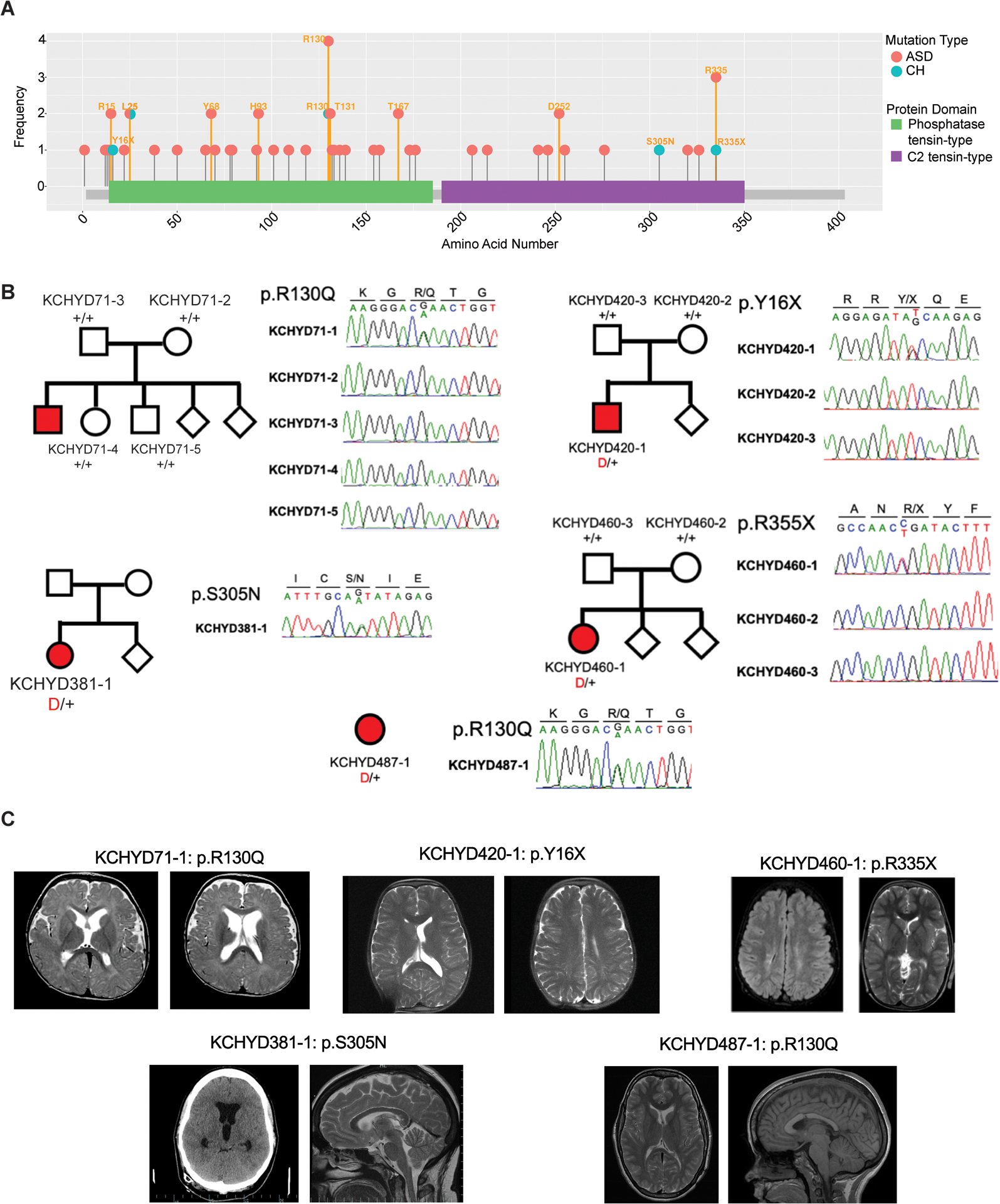
(A) PTEN mutations identified in individuals with ASD (pink) and CH (blue) are shown in relation to PTEN functional domains. This figure was generated using the MutPlot program [138] to map the missense and truncating mutations identified in our literature search (Table S1 in the supplemental information online) onto the human PTEN protein domains reported in UniProt [139]. Splice site mutations are not shown, but are listed in Table S1 in the supplemental information online. Mutation frequency at each residue (based on Table S1 in the supplemental information online) is shown on the y axis. Additional information about clinical features associated with mutations can be found in Table S1 in the supplemental information online. (B) Family pedigrees and Sanger sequencing electropherograms of individuals who underwent neurosurgical treatment for sporadic CH and harbor PTEN mutations, corresponding to reported mutations from Table 1. (B) Adapted, with permission, from [24]. Abbreviation: PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog. (C) Representative T1 or T2-weighted axial and sagittal brain MRIs or head CT images of neurosurgically treated CH patients harboring indicated PTEN mutations, adapted, with permission, from [24].
