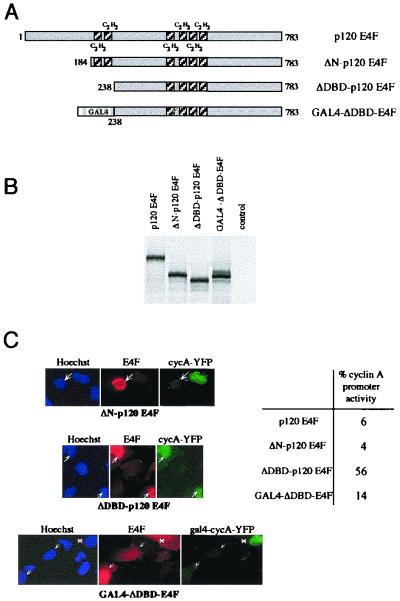
FIG. 8.
p120E4F DNA binding activity is required for cyclin A transcriptional repression. (A) Amino-terminal deletion mutants of p120E4F. Deletion of the first 183 aa of p120E4F (ΔN-p120E4F mutant) preserves the integrity of the six zinc finger domains. The ΔDBD-p120E4F mutant corresponds to a polypeptide (aa 238 to 783) which lacks the two p120E4F amino-terminal zinc finger motifs. The C2H2 zinc finger motifs are shown as shaded boxes. The GAL4-ΔDBD-E4F fusion protein contains the GAL4 DNA binding domain (aa 1 to 147) fused N terminally to ΔDBD-p120E4F. (B) Expression of the mutants in vitro. Full-length p120E4F as well as the mutants ΔN-p120E4F, ΔDBD-p120E4F, and GAL4-ΔDBD-E4F were in vitro translated and analyzed by SDS-PAGE along with unprogrammed reticulocyte lysates (control). (C) The two p120E4F N-terminal zinc finger domains are required for repression of cyclin A transcription. U2OS cells were cotransfected with expression vectors for either pCycA-nucYFP and p120E4F, ΔN-p120E4F, or ΔDBD-p120E4F or for gal4-cycA-YFP and GAL4-ΔDBD-E4F. The panels show E4F immunodetection, YFP expression, and Hoechst staining. Arrows indicate E4F-transfected cells. A transfected cell with a cytosolic localization of GAL4-ΔDBD-E4F fusion protein is indicated by the asterisk. The percentage of cells that contain an active cyclin A promoter, as estimated by expression of YFP, is indicated (about 100 counted cells).