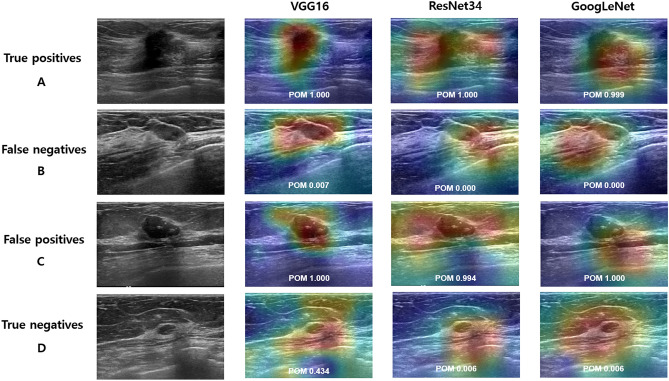
Figure 3.
Classification results with class activation map (CAM) using the weakly-supervised deep learning (DL) algorithm on external validation set. Examples of true-positive (A), false-negative (B), false-positive (C), and true-negative (D) are shown for each network (VGG16, ResNet34, and GoogLeNet). (A) Ultrasound images show a 17-mm irregular, spiculated invasive ductal carcinoma, which was predicted as malignancy with probability of malignancy (POM) of 1.00, 1.00, and 0.999 in VGG16, ResNet34, and GoogLeNet, respectively. (B) Ultrasound images show an 11-mm oval, circumscribed, isoechoic mucinous carcinoma, which was predicted as benign with POM of 0.007, 0.000, and 0.000, respectively. (C) Ultrasound images show a 29-mm oval, hypoechoic mass with macrocalcifications considered as benign (unchanged during the 46-month follow-up period), which was predicted as malignancy with POM of 1.000, 0.994, and 1.000, respectively. (D) Ultrasound images show a 6-mm oval, circumscribed mass considered as benign (unchanged during the 55-month follow-up period), which was predicted as benign with POM of 0.434, 0.006, and 0.006, respectively.