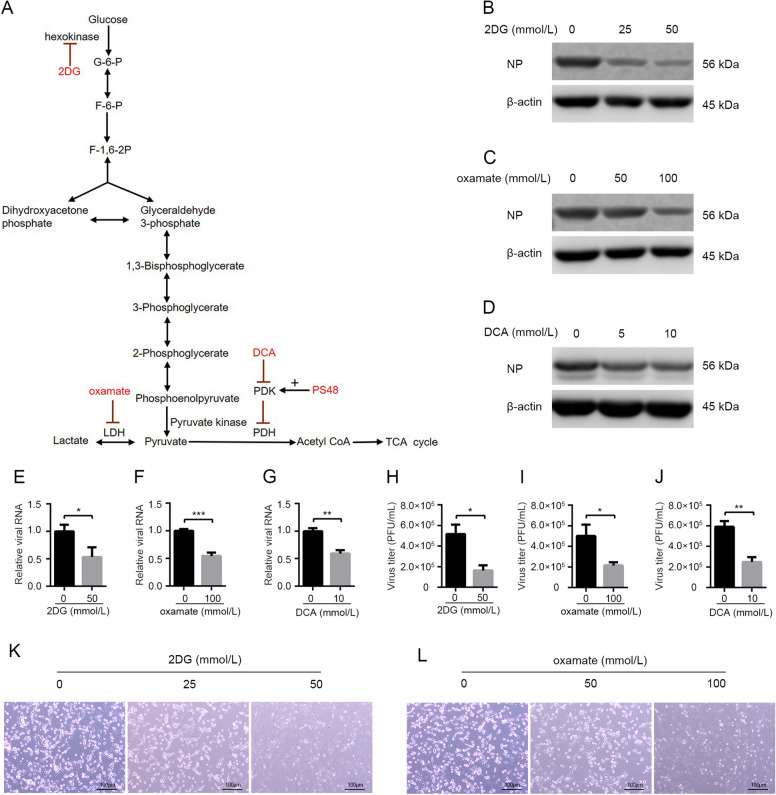
Fig. 2.
Glycolytic inhibitors impair H1N1 replication and alleviate virus-induced cell injury. A Schematic overview of the glucose metabolism and the functional targets of glycolytic inhibitors (2DG, oxamate, and DCA) and enhancer (PS48) used in this study. B–L A549 cells were infected with H1N1 at an MOI of 1, with or without glycolytic inhibitors treatment at the same time. B–D Cells were harvested at 24 h p.i., and intracellular NP levels were measured by Western blotting. E–G Cells were harvested at 24 h p.i., and intracellular viral RNA (M) levels were measured by qRT-PCR. β-actin expression was used as an internal control. H–J Cell supernatant were harvested at 24 h p.i., and viral titer levels were measured by plaque forming unit assay. K, L The morphological changes of A549 cells at 24 h p.i. under a phase contrast microscope were shown. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.