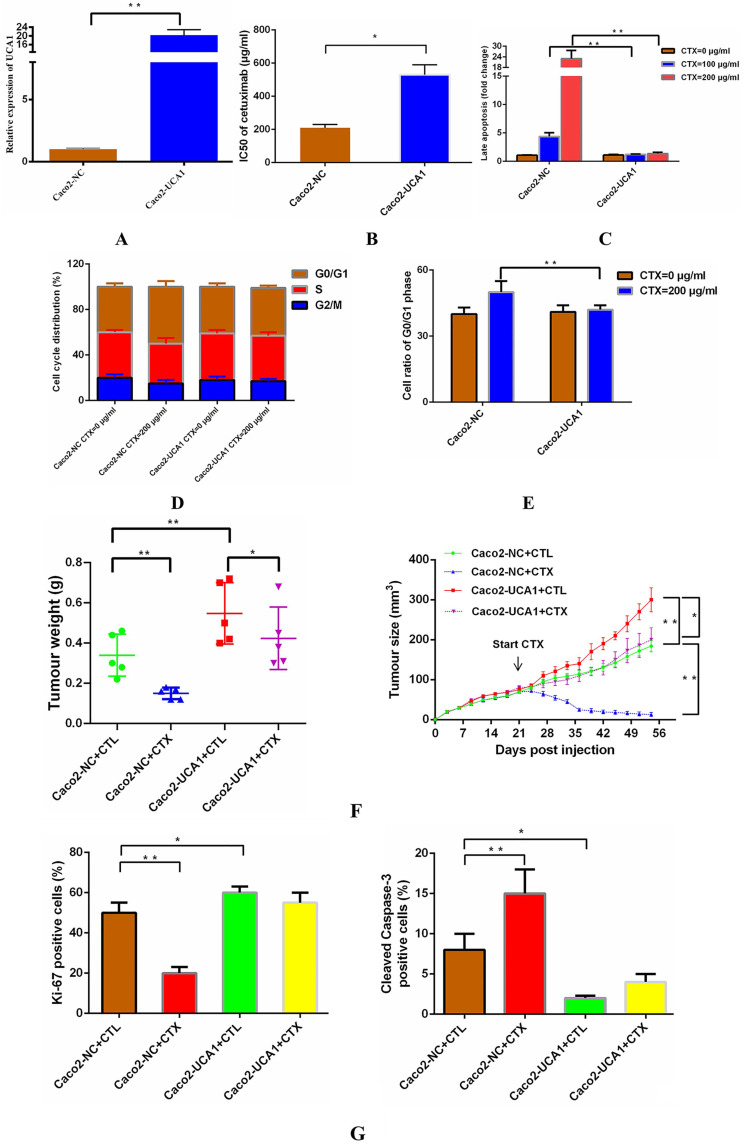
Figure 1.
UCA1 promotes cetuximab resistance in vitro and in vivo. (A) UCA1 expression was dramatically upregulated in Caco2-UCA1 cells. (B) The IC50 values of cetuximab were significantly higher in Caco2-UCA1 cells than in Caco2-NC cells. (C) The percentage of late apoptotic cells was significantly higher in Caco2-NC cells than in Caco2-UCA1 cells. (D-E) UCA1 overexpression did not cause significant changes in the cell cycle distribution, while G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest was inhibited by cetuximab. (F) UCA1 affects cetuximab resistance in vivo. (G) Xenografts from the Caco2-NC group demonstrated less Ki-67 staining (left) and increased cleaved caspase-3 staining (right) than those observed in the control group after cetuximab treatment. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.