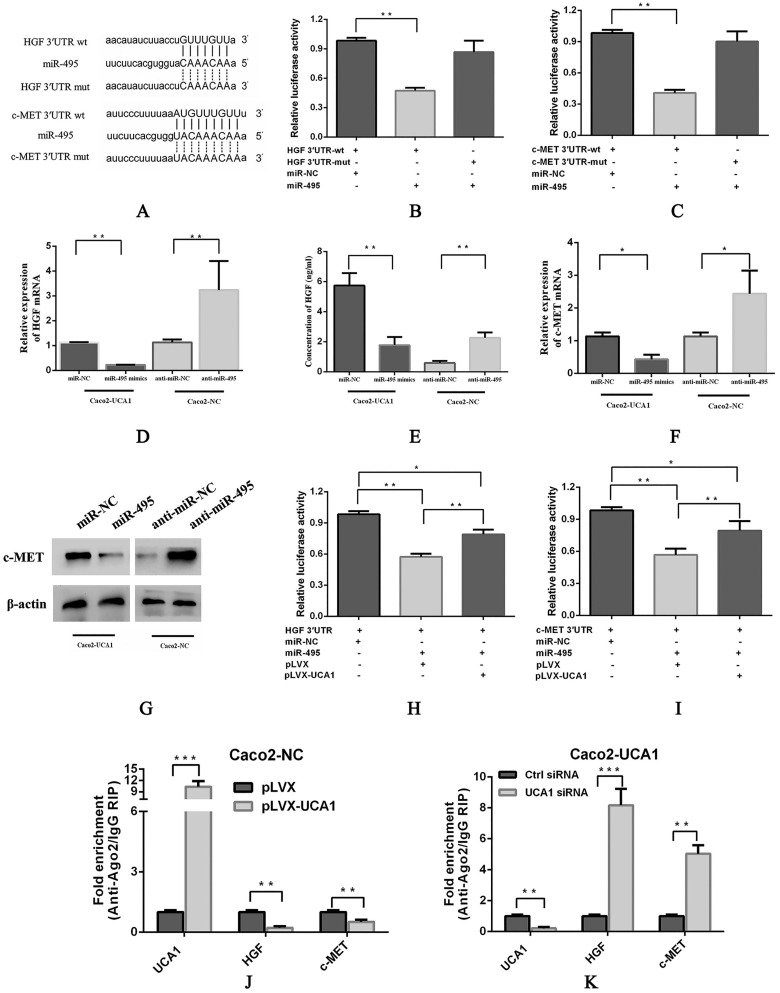
Figure 3.
UCA1 modulates HGF and c-MET expression in a miR-495-dependent manner. (A) Schematic comparison between HGF (top) or c-MET (bottom) and the “seed sequence” of miR-495. miR-495 significantly inhibited the luciferase activity of the pmirGLO-HGF 3'UTR-wt (B) and pmirGLO-c-MET 3'UTR-wt (C) reporters but not that of the pmirGLO-3'UTR-mut reporter. miR-495 overexpression in Caco2-UCA1 cells decreased the mRNA expression (D) and secreted protein levels of HGF (E) and the mRNA expression (F) and protein levels of c-MET (G), while miR-495 knockdown increased HGF (D) and c-MET mRNA (F) and protein levels (E, G) in Caco2-NC cells. β-actin was used as an internal control. In the presence of UCA1, the expression of reporter genes was restored in the pmirGLO-HGF 3'UTR (H) or pmirGLO-c-MET 3'UTR group (I). (J) UCA1 overexpression led to enriched levels of Ago2 on UCA1 transcripts but substantially decreased those on HGF and c-MET transcripts. (K) UCA1 knockdown induced a significant increase in Ago2 recruitment to HGF and c-MET transcripts. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0001.