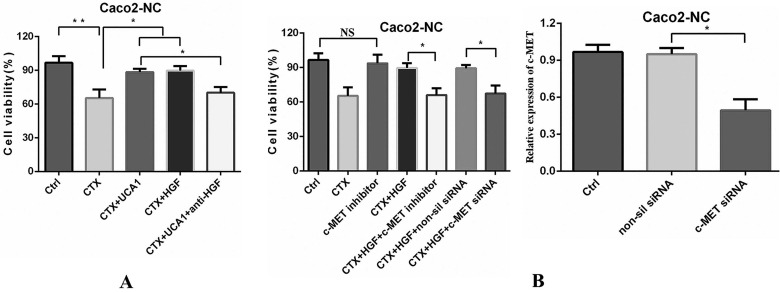
Figure 4.
UCA1-mediated HGF-dependent MET activation rescues Caco2-NC cells from cetuximab inhibition. (A) Cetuximab (200 µg/ml) decreased cell viability, whereas cell proliferation significantly increased after the combination of cetuximab (200 µg/ml) with pLVX-UCA1 or HGF (10 µg/ml) treatment compared to cetuximab alone treatment. Treatment with an HGF neutralizing antibody (30 µg/ml) significantly hampered cell proliferation caused by UCA1 overexpression. (B) Left panel: Caco2-NC cells were treated with a combination of cetuximab (200 µg/ml) and HGF (10 µg/ml) with or without PHA-665752 (0.4 µM), and PHA-665752 completely abrogated the rescue effect of HGF and essentially restored the cetuximab-mediated inhibitory effects. SiRNA-mediated c-MET expression downregulation (right panel) abolished HGF-induced cetuximab resistance. NS, not significant. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.