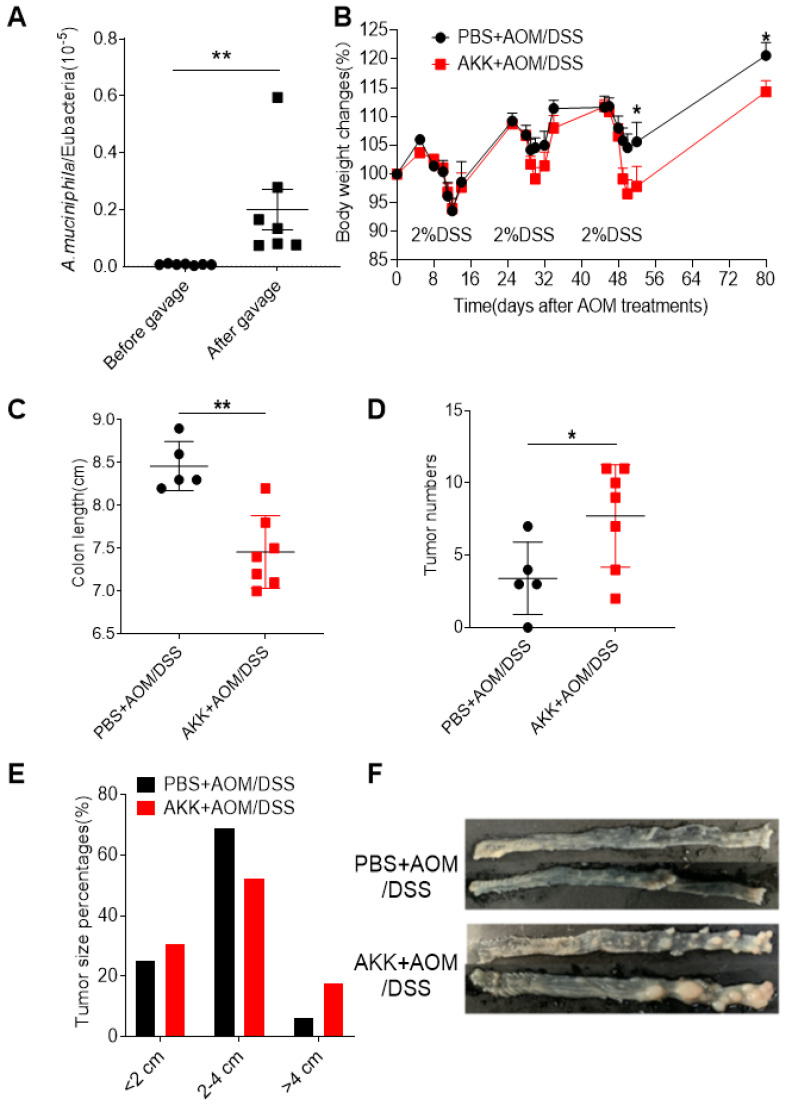
Figure 1.
Akkermansia muciniphila administration enhanced the susceptibility of mice to colitis-related colorectal cancer (CAC). C57BL/6 mice were orally administrated with A. muciniphila or PBS and treated with AOM/DSS to induce CRC. Bacterial colonization was validated in the feces collected before and after gavage by quantitative PCR. Mouse body weights were monitored during the AOM/DSS treatment. After 80 days, the mice were sacrificed, and the colons were collected to measure the tumor burden. A. The number of A. muciniphila in the feces of mice before and after gavage; B. body weight change; C. Colon length; D. The number of colon tumors; E. Tumor diameter; F. Representative photos of colon tumors. The data of A-D were represented by the Mean ± SEM, PBS+AOM/DSS, n=5; AKK+AOM/DSS, n=7. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, A, C, D. Unpaired student T test, B.Two-way ANOVA analysis. The experiments were repeated twice independently.