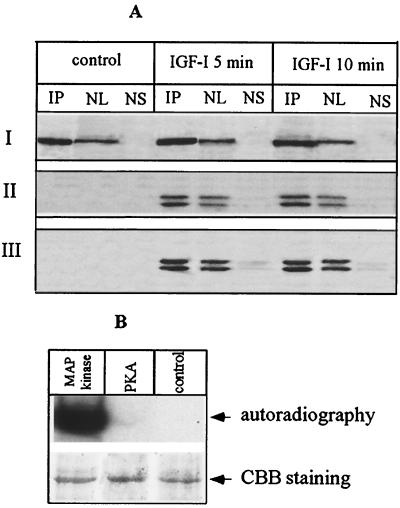
FIG. 4.
Nuclear PLC β1 is the direct target of ERK in vivo and in vitro. (A) Cells overexpressing PLC β1 were incubated without or with IGF-I for different periods. The nuclei were purified from these cells and then lysed with IP buffer. Aliquots of nuclear lysate were subjected to IP by anti-PLC β1 MAb. The nuclear supernatant was saved after recovery of IP complexes. IP complexes were released from protein A/G Sepharose beads by incubating with 50 μl of SDS loading buffer at 95°C for 5 min. Nuclear lysate (NL) (20 μg), 25 μl of nuclear supernatant after recovery of IP complexes (NS), or 25 μl of IP complexes was separated by SDS–8% PAGE and blotted with either anti-PLC β1 (panel I), anti-phospho-p42/p44 MAP kinase antibody (panel II), or anti-p42/p44 MAP kinase (panel III). The result is representative of three independent experiments. (B) PLC β1 was expressed and purified using a baculovirus-based system as described in the text. A 500-ng portion of the purified protein was phosphorylated in vitro using the indicated kinases, separated by SDS–8% PAGE, and visualized by either autoradiography or Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining.