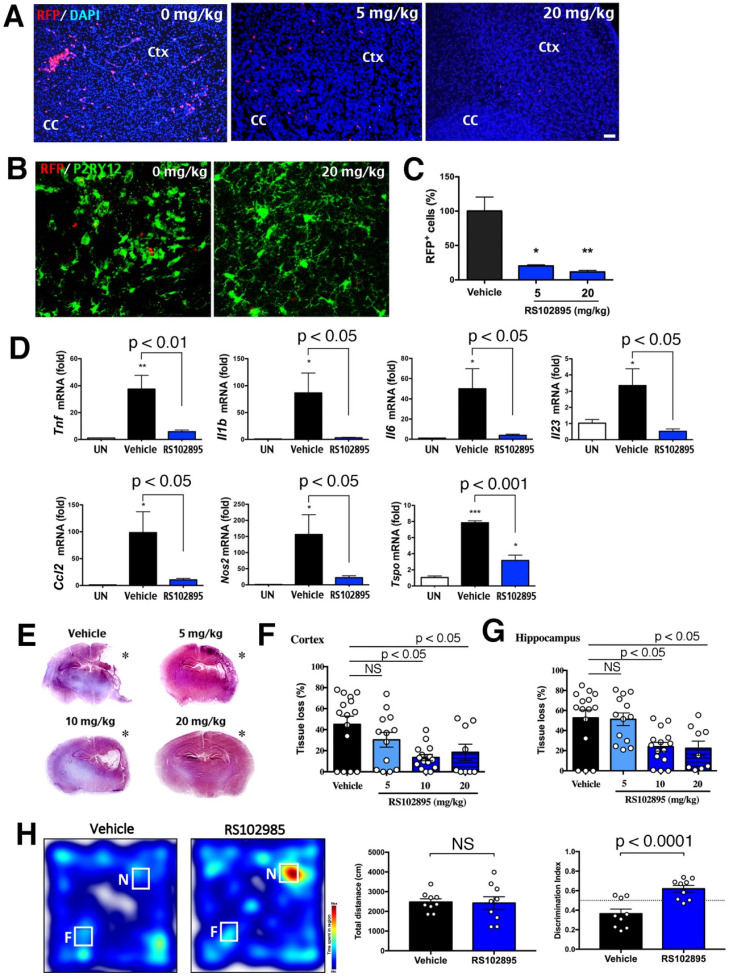
Figure 7.
Protection against neonatal LPS/HI injury with CCR2-inhibitor treatment. (A, C) CCR2RFP/+ mice receiving two doses of 5 or 20 mg/kg RS102895 (IP) within 1 h post-LPS/HI contained significantly fewer RFP+ cells than vehicle-treated mice 24 h later (n = 8 for vehicle, n = 3 for RS102895-5 mg/kg and n = 5 for RS102895-20 mg/kg). (B) RS102895 (20 mg/kg x 2) treatment showed more ramified microglia by Tmem119 staining than the vehicle group. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) RT-qPCR analysis shows that RS102895 treatment (10 mg/kg) significantly attenuated LPS/HI-induced Tnf, Il1b, Il6, Il23, Ccl2, Nos2 and Tspo transcripts at 24 h recovery (n = 4 for untouched, n = 4 for vehicle and n = 3 for RS102895-10mg). (E) Representative images of vehicle-versus-RS102895 treated C57BL/6 mice at 7 d after neonatal LPS/HI injury. (F-G) Quantification shows significant reduction of cerebral cortex (F) and hippocampus (G) tissue loss in the mice receiving 5, 10 or 20 mg/kg RS102895 treatment (2 doses), when compared to vehicle-treated mice (n = 15 for vehicle, n = 13 for RS102895-5mg, n = 15 for RS102895-10mg and n = 9 for RS102895-20mg). (H) Representative heat map of the time spent with a novel (N) or familiar (F) object by vehicle-versus-RS102896 treated mice (10 mg/kg) at 45 d post-LPS/HI injury. Quantification showed an improved discrimination index (the ratio of time spent with the novel over the time with the familiar object) in RS102896-treated mice compared with vehicle-treated mice (p < 0.0001 by unpaired t-test; n = 9 for each group). The dash-line indicates a discrimination index at 0.5. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 versus vehicle-treated control by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc analysis.