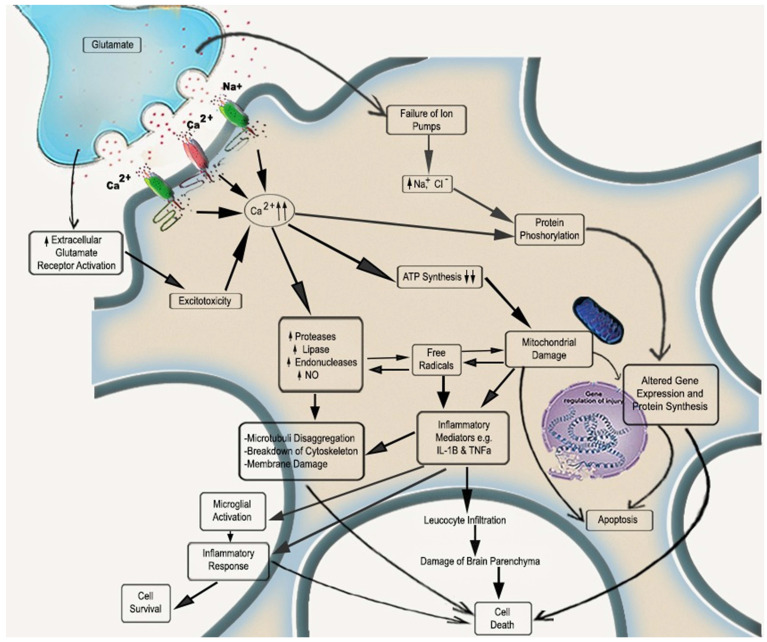
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms initiated during acute ischemic stroke. With the disruption of cerebral blood availability, energy production decreases. In the scarcity of energy supply, the ion pumps fail along with the generation of free oxygen radicals, mitochondrial injury, leukocyte infiltration, and release of excitotoxins. Over accumulation of calcium leads to activation of phospholipases and proteases followed by membrane damage and cytoskeleton damage that ultimately leads to cell death. The inflammatory pathway may also be involved in cell survival by microglial activation.