Figure 1.
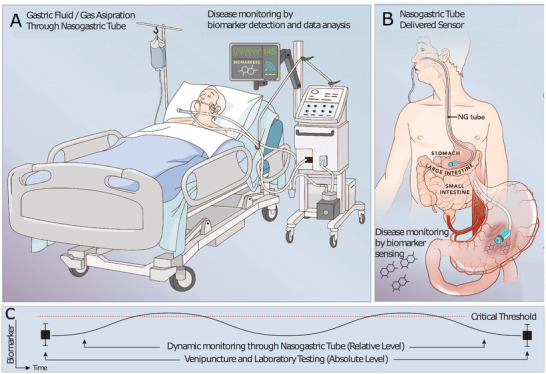
Schematic diagram demonstrating the concept to monitor systemic biomarkers with nasogastric (NG) compatible sensors. Gastric fluid (GF)/gas contains systemic biomarkers, and these can be monitored through A) aspiration and continuous analysis with ex vivo systems or B) intragastric sensor placements via NG tubes. The sensor resides in the stomach and is immersed in GF which contains systemic biomarkers. C) Demonstrates a use case in which a biomarker is monitored throughout the time period in between classical clinical laboratory testing to increase responsiveness of clinical care teams.
