Figure 1.
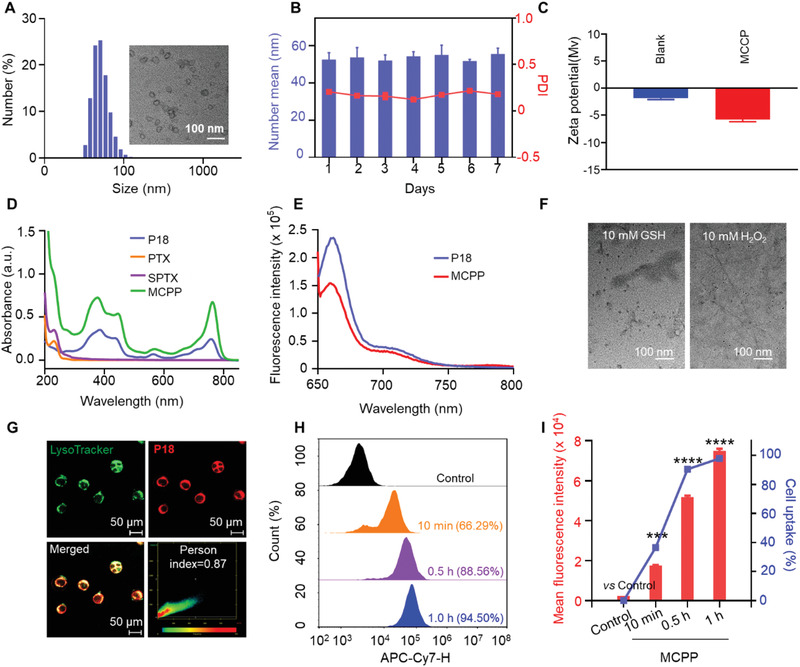
Characterization and cellular uptake behaviors of MCPP nanoparticles. A) DLS profile and TEM image of MCPP NPs. B) The micellar stability of MCPP for 7 days (n = 3). C) Zeta potential of MPEG‐CPPA‐b‐P (M4) (Blank) and MCPP in water (n = 3). D) UV–vis absorption spectra of different formulations. E) Fluorescence emission spectra of free P18 and MCPP in DMF. F) TEM images of MCPP micelles after GSH or H2O2 treatment. G) Colocalization of MCPP with lysosomes in CT26 cells; CT26 cells were incubated with MCPP for 6 h, then treated with LysoTracker (green fluorescence) for 15 min and observed by CLSM. H) Flow cytometry analysis of the MCPP signal in CT26 cells at various time points. I) Quantitative analysis of the flow cytometry results revealed that the cellular uptake of MCPP occurred in a time‐dependent manner. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001).
