Figure 3.
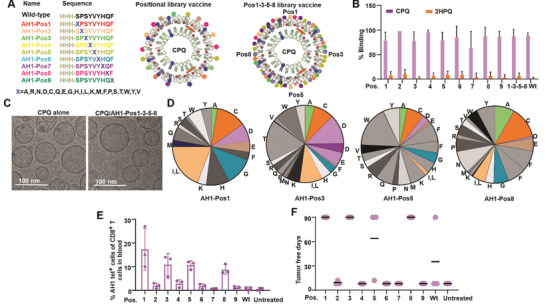
AH1‐Pos1, AH1‐Pos3, AH1‐Pos5, and AH1‐Pos8 library vaccine immunogens induced more AH1‐specific CD8+ T cells than the wild‐type epitope and protected mice from tumor challenge. A) Scheme of CPQ vaccines that made of one AH1 positional library or 4 AH1 positional libraries. B) Percentage of AH1 peptide libraries bind to CPQ and 2HPQ liposomes. Error bars show mean ± std. dev. for n = 3 triplicate experiments. C) Cryo‐electron micrographs of CPQ and CPQ/AH1‐Pos1‐3‐5‐8. Representative images from a single experiment are shown. D) Amino acid distribution of AH1‐Pos1, AH1‐Pos3, AH1‐Pos5 and AH1‐Pos8 positional library. BALB/c mice were untreated or vaccinated with CPQ and AH1 wild‐type peptide or AH1 peptide libraries on days 0 and 7, then blood was collected for analysis and CT26 tumor cells were inoculated subcutaneously on day 14. E) Percentage of AH1 tet+ cells in the CD8+ T cell population. Error bars show mean ± std. dev. for n = 3. F) Tumor free days. The experiment was performed with n = 3 independent mice and the line shows the mean.
