Figure 5.
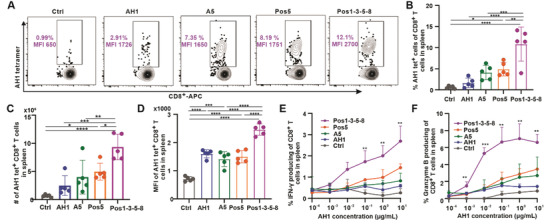
AH1 positional library immunogens induced CD8+ T cells with higher affinity to the AH1 tetramer and generated a greater frequency of cytokines compared to the wild‐type epitope. BALB/c mice were inoculated with CT26 cells subcutaneously on day 8 and then untreated or injected with vaccine on days 8 and 15. Splenocytes were collected on day 23. Flow cytometry gating (A) and percentage (B) of AH1 tet+ cells in the CD8+ T cell population. C) Number of AH1‐tet+ CD8+ T cells in spleen. D) Geometric medium fluorescence intensity (MFI) of AH1‐tet+ CD8+ T cells. Splenocytes were stimulated with different concentrations of the wild‐type AH1 peptide, followed by analysis of IFN‐γ and granzyme B expression by intracellular staining. E) Percentage of IFN‐γ‐producing cells and F) percentage of granzyme B‐producing cells in the CD8+ T cell population. Error bars in B, C, D, E, F show mean ± std. dev. for n = 5 mice. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001, analyzed by (B, C, D) one‐way ANOVA with E,F) Tukey multiple comparisons post‐test or one‐way ANOVA with Dunnett comparisons post‐test. Asterisks in panel E and F indicates statistically significant differences between indicated group and control group with indicated AH1 concentration.
