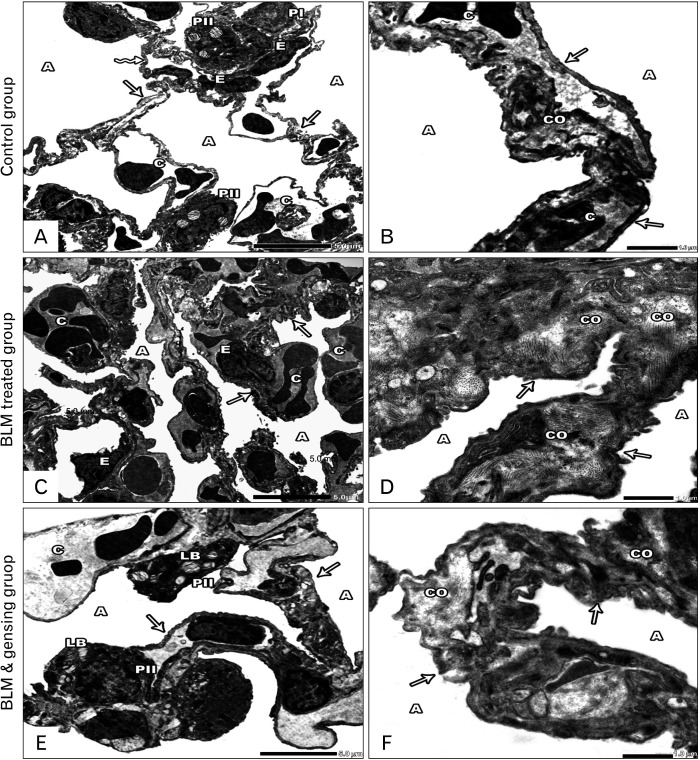
Fig. 5.
Photos of ultrathin sections of lung sections. (A, B) Control sections: (A) Lung alveoli (A) are lined by type I (PI) and type II (PII) pneumocytes. The alveoli are separated by interalveolar septa, is formed of thin (arrows) & thick portions (zigzag arrow) with the presence of blood capillaries (C) lined by endothelial cells (E). (B) Lung alveoli (A) separated by interalveolar septa (arrow) with minimal collagen fiber (CO) and blood capillaries (C). (C, D) Bleomycin (BLM) treated sections: (C) Collapsed alveoli (A), thickened interalveolar septa (arrows) with congested blood capillaries (C) and distorted endothelial lining (E) are seen. (D) Collapsed lung alveoli (A) are separated by thickened interalveolar septa (arrows) with massive collagen fiber deposition (CO). (E, F) BLM & ginsenosides treated sections: (E) Intact & inflated alveoli (A) separated by thin interalveolar septa (arrows) with mild congested blood capillaries (C). The alveoli are lined by type I (PI) & type II (PII) pneumocytes with its characteristic lamellar bodies (LB). (F) Inflated Lung alveoli (A) separated by interalveolar septa (arrows) with mild collagen fiber (CO) deposition. (A, C, E) ×6,000; (B, D, F) ×20,000.