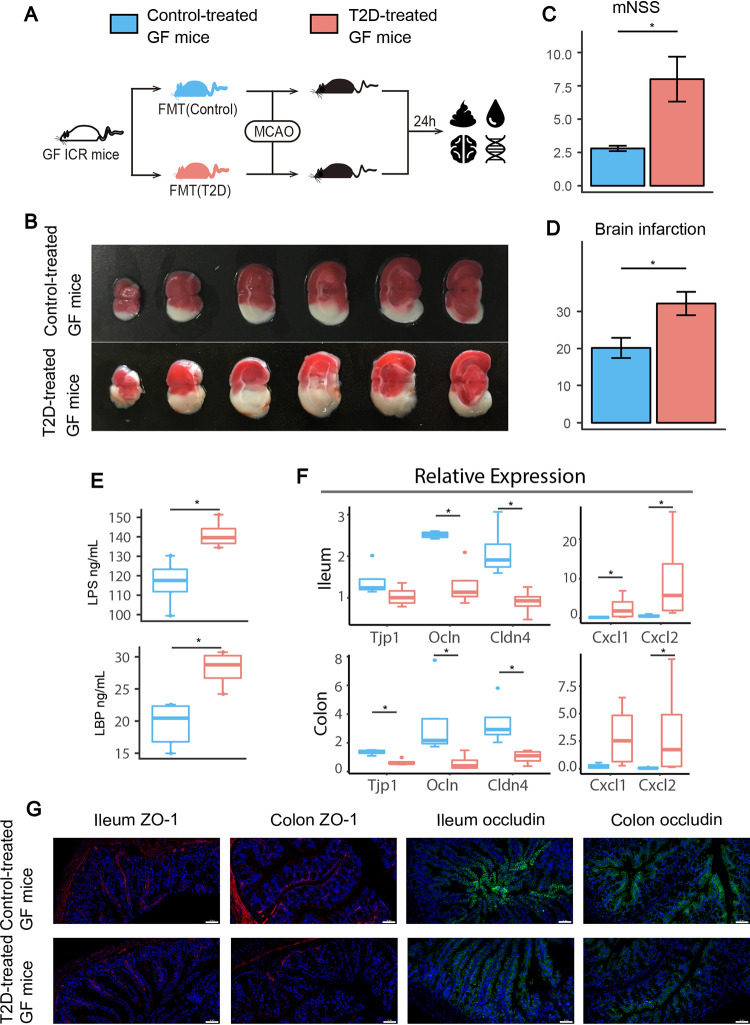
FIG 4.
T2D-treated GF mice exhibited exacerbated cerebral injury and gut barrier dysfunction. (A) Experimental design of FMT and MCAO surgery in GF mice. (B) Representative images of TTC-stained coronal brain sections. (C–D) Comparison of the brain infarction ratio and mNSS between GF mice transplanted with fecal samples from healthy controls (n = 5, blue) and T2D patients (n = 4, red). (E) Serum LBP and LPS levels in control and T2D-treated GF mice. (F) Relative expression of the Tjp1, Ocln, Cldn4, Cxcl1, and Cxcl2 genes and (G) immunofluorescent staining for occludin and ZO-1 (magnification, ×200) in mouse ileum and colon tissues. Scale bar 50 μm. *, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.01 based on the Wilcoxon rank sum test. FMT, fecal microbiota transplantation; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; mNSS, modified neurological severity score.