Figure 1.
Single-cell RNA-seq of iPSC-derived neurons
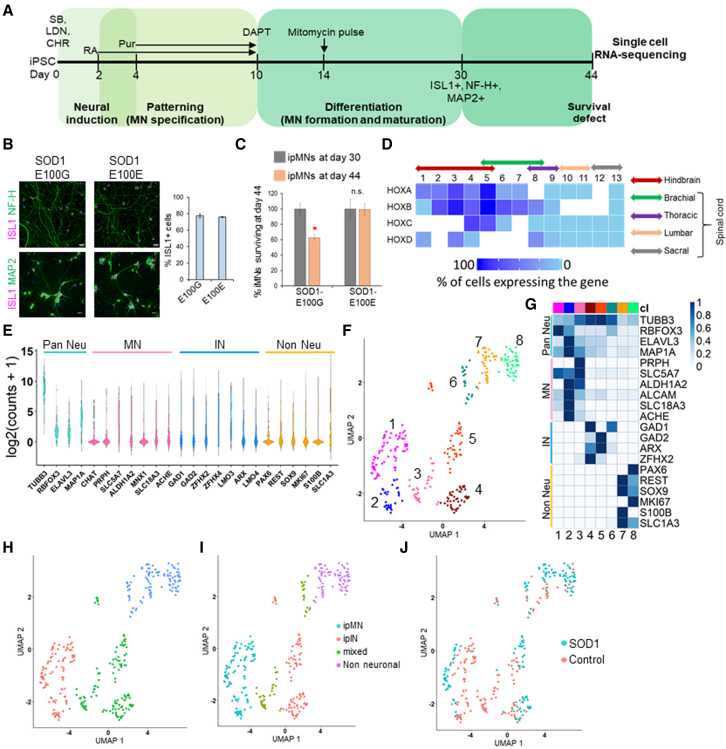
(A) Differentiation protocol used to derive MNs from human iPSCs. Numbers on the horizontal line indicate days. SB, SB431542; LDN, LDN193189; CHR, CHIR99021; RA, retinoic acid; Pur, purmorphamine.
(B) ipMNs at day 30 stain positive for ISL1, NF-H, and MAP2. Scale bar indicates 50 μm.
(C) MNs (ISL1+) were counted at d30 and d44 of the differentiation protocol. D44 MN counts were normalized to d30 counts. SOD1 E100G indicates the MNs derived from mutant SOD1 iPSC. SOD1 E100E indicates the isogenic corrected control MNs. Error bars shown are SEM, n = 3 independent biological replicates. ∗p < 0.01; n.s., not significant.
(D) Heatmap displaying percentage of cells expressing specific HOX genes. White space indicates that the corresponding HOX paralog is not expressed in humans. Colored solid arrows indicate the HOX code for specific spinal segments along the rostro-caudal axis.
(E) Violin plots displaying distribution of expression levels of displayed markers across all cells.
(F) UMAP plot showing clustering of single cells.
(G) Normalized mean expression of neural markers across all eight clusters (cl). Clusters have been coded by numbers (at the bottom) and by color (at the top). These correspond to the numbers and colors shown in (F).
(H) Partition analysis shows the MN cluster 3 associating closely with IN clusters 4 and 5, while IN cluster 6 associates with non-neuronal clusters 7and 8.
(I) UMAP plot showing classification of single cells into MNs, Ins, and non-neuronal cells based on marker expression.
(J) UMAP plot showing distribution of the identified cell types among the ALS SOD1 E100G (SOD1) and isogenic SOD1 E100E control samples.
See also Figures S1 and S2.