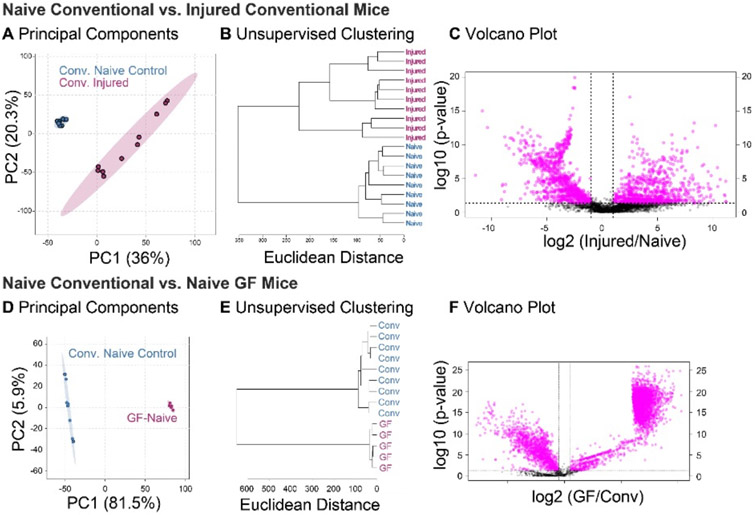
Figure 3:
Global metabolomic profiles of synovial fluid are driven by both injury and germ-free status. (A) Principal components analysis (PCA) finds complete separation between injured and naïve metabolomic profiles of conventional mice, with 36% and 20.3% of the variance associated with PC1 and PC2, respectively. (B) Conventional injured and naïve mice separate into two distinct clusters by unsupervised hierarchical cluster analysis. (C) 1038 metabolite features were significantly downregulated, and 971 metabolite features were significantly upregulated in Conv-inj compared to Conv-ctrl mice. (D) PCA finds clear separation between synovial fluid metabolomic profiles of germ-free and conventional mice, with 81.5% and 5.9% of the variance associated with principal components (PC) 1 and 2, respectively. (E) Unsupervised hierarchical clustering analysis finds distinct clusters between conventional and germ-free mice. (F) Volcano plot analysis found 4357 metabolites significantly different between germ-free and conventional mice. 1279 metabolites were significantly downregulated, and 3078 metabolites were significantly upregulated in naïve GF compared to naïve conventional mice.