Figure 1. Overview of the gene locus and allelic variation.
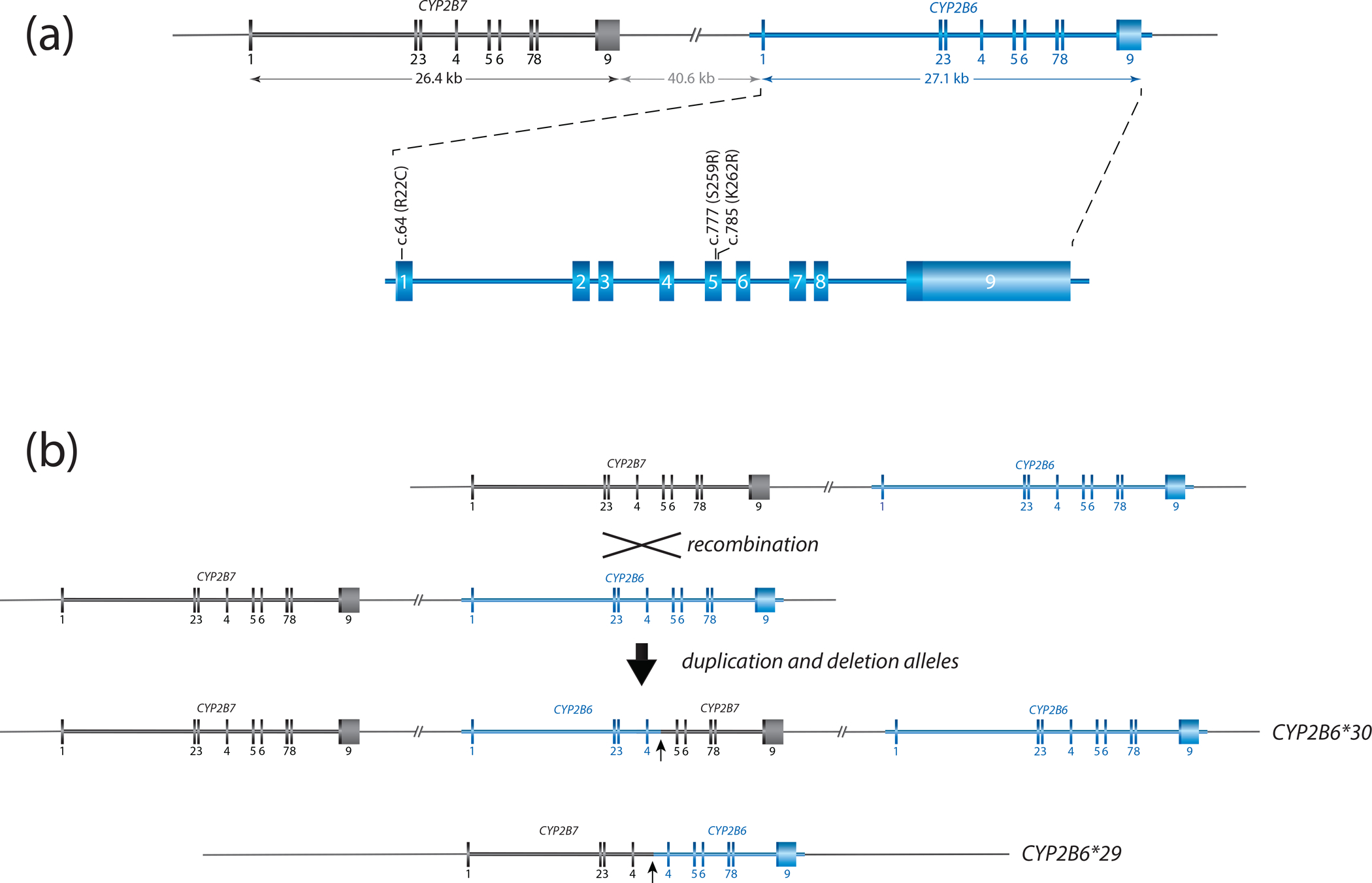
Panel A provides a graphical overview of the CYP2B gene locus containing CYP2B6 and CYP2B7. Both are encoded on the forward strand. CYP2B6 is composed of nine exons, covering 27.1 kb. The nonfunctional CYP2B7 pseudogene spans 26.4 kb. The two genes are interspersed by about 41 kb. Exonic sequences differ by only a few bases: exon 1 (9 base differences), exon 2 (9), exon 3 (6), exon 4 (13), exon 5 (2), exon 6 (4), exon 7 (10), exon 8 (3) and exon 9 (5). The enlarged region of CYP2B6 shows the location of selected sequence variants. c.64C>T (p.R22C) and c.777C>A (p.S259R) are SNVs defining CYP2B6*2 and *3 while c.785A>G (p.K262R) is part of multiple haplotypes including *4 and *6.
Panel B illustrates a reciprocal recombination event resulting in a partial deletion (CYP2B6*29) and a duplication (CYP2B6*30) event. CYP2B6*29 and *30 harbor 23 and 15 amino acid changes, respectively (see Structural Variation document for details). The recombination is facilitated by a 529 bp long intron 4 region with high homology between CYP2B6 and CYP2B7. Both recombination products are characterized by the presence of gene copies consisting of CYP2B7 and CYP2B6 as shown.
