Fig. 2. XN, DXN and TXN decrease hippocampal ceramides in HFD-fed mice.
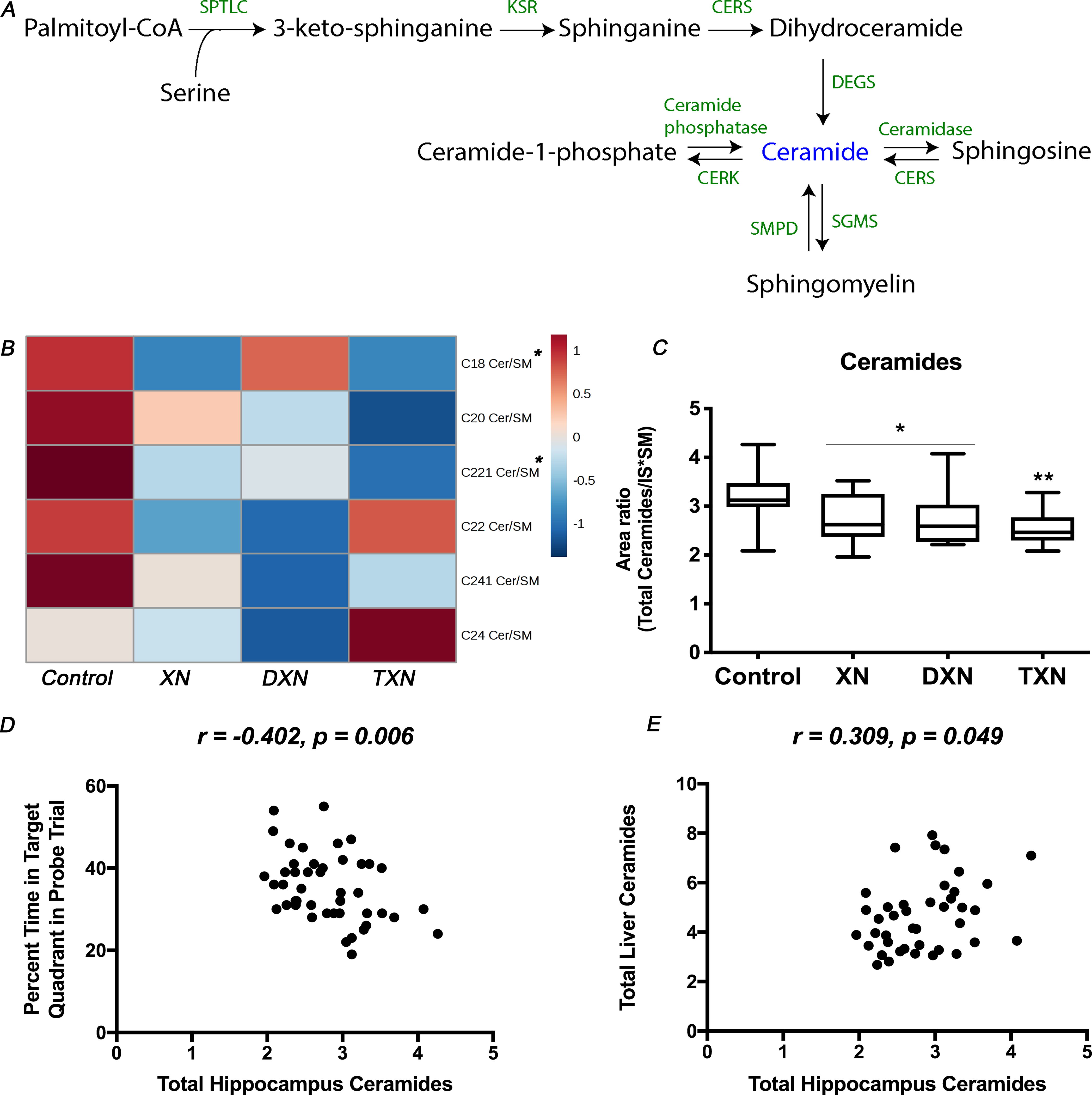
(A) Ceramide metabolism in mammalian cells: ceramides can be synthesized de novo from fatty acids or sphingosines through the actions of serine palmitoyl transferase and ceramide synthases, which starts on the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum. Ceramides can also be generated from SM catabolism by sphingomyelinases or through degradation of complex sphingolipids in late endosomes and lysosomes. (B) Heatmap of annotated ceramide species in the hippocampus of control and treated mice. (C) Total amounts of ceramides in the hippocampus of control and treated mice (n = 9–12 per group). (D) Correlation between relative abundance of ceramides in the hippocampus and percent time in the target quadrant during the probe trial (r = −0.402, p = 0.006, n = 45 data points). (E) Correlation between relative abundance of ceramides in the hippocampus and in the liver (r = 0.309, p = 0.049, n = 41 data points). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
