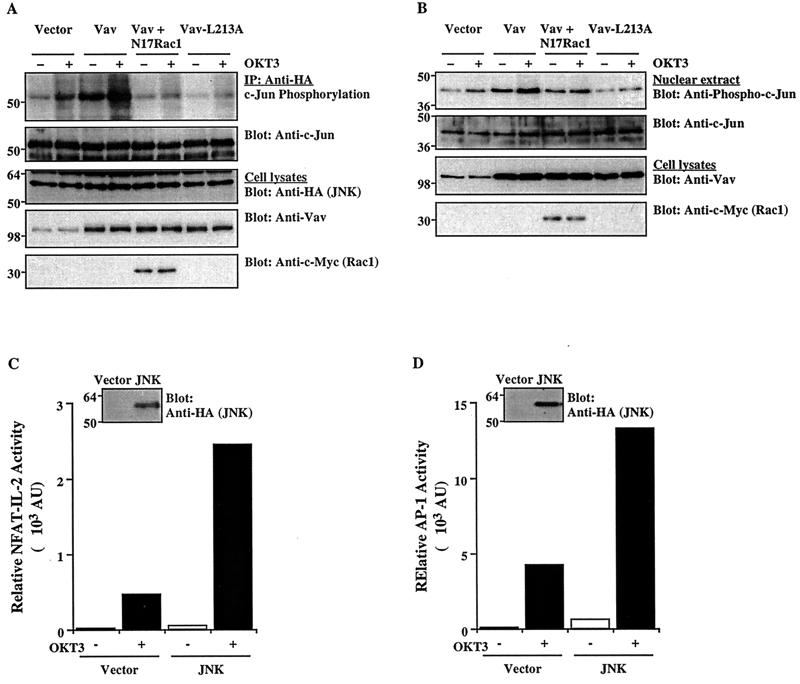
FIG. 5.
Effect of Vav on JNK activation and c-Jun phosphorylation. (A) Cells were cotransfected with an HA-tagged JNK1 plasmid plus the indicated combinations of Vav, Vav-L213A, and/or N17Rac1 (5 μg each). After 24 h, the cells either were left unstimulated or were stimulated with cross-linked OKT3. JNK1 was immunoprecipitated (IP) from cell lysates with an anti-HA MAb and subjected to an in vitro kinase assay using GST–c-Jun as a substrate. The SDS-PAGE-separated kinase reaction was visualized by autoradiography (top panel), followed by immunoblotting with an anti-c-Jun antibody (second panel from top). Total cellular extracts were immunoblotted with anti-HA, anti-Vav, or anti-c-Myc antibodies (bottom three panels). The results shown are representative of four separate experiments. (B) Cells were transfected and stimulated as described for panel A. Nuclear extracts were prepared, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted with anti-phospho-c-Jun or anti-c-Jun antibodies (top two panels). Total cellular extracts from the same groups were immunoblotted with anti-Vav or anti-c-Myc antibodies (bottom two panels). (C and D) Cells were cotransfected with NFAT–IL-2–Luc or AP-1–Luc reporter plasmids plus empty pcDNA3 or an HA-tagged JNK1 plasmid. Reporter activity in unstimulated or OKT3-stimulated cells was determined as described in the legend to Fig. 1. AU, arbitrary units. Samples of the same lysates were immunoblotted with an anti-HA MAb to detect JNK expression (insets). The results are representative of three separate experiments. The positions of molecular weight standards (in thousands) are shown.