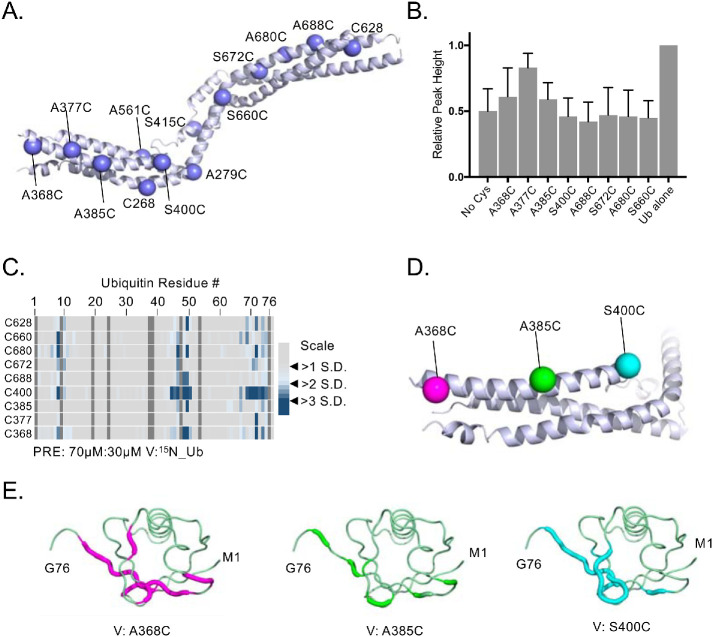
FIGURE 2:
Locating the binding regions of 15N-Ub on the HD-PTP V domain by PRE experiments. (A) Position of single-amino-acid replacement mutations comprising a set of single cysteine–containing VHDPTP variants. (B) Relative average HSQC peak heights (±SD) of all residues of 30 µM 15N-Ub HSQC spectra alone or in the presence of MTSL-labeled 70 µM HD-PTP variant proteins in the presence of 2 mM ascorbate. Binding of VHDPTP broadens 15N-Ub amide peaks, resulting in lower relative peak heights. (C) The indicated single cysteine–containing V domain variants were spin labeled with MTSL and incubated with 15N-Ub at a ratio of 70 µM:30 µM (V:Ub) in the absence and presence of reduction by ascorbate. PRE effects, measured by the ratio of peak intensities before and after reduction, are plotted by an increase in color intensity indicating those that were 2–4 SDs from the mean change. (D) Position of three cysteine substitutions on the N-terminal helix of HD-PTP that had the largest PRE effects on 15N-Ub labeled in magenta, green, and cyan, respectively. (E) Backbone amides of Ub undergoing largest PRE effects (>2 SD above the mean) when bound to HD-PTP spin labeled at residue 368, 385, or 400. These PRE effects were mapped onto Ub backbone (PDB:1UBQ) in magenta, green, and cyan, respectively.