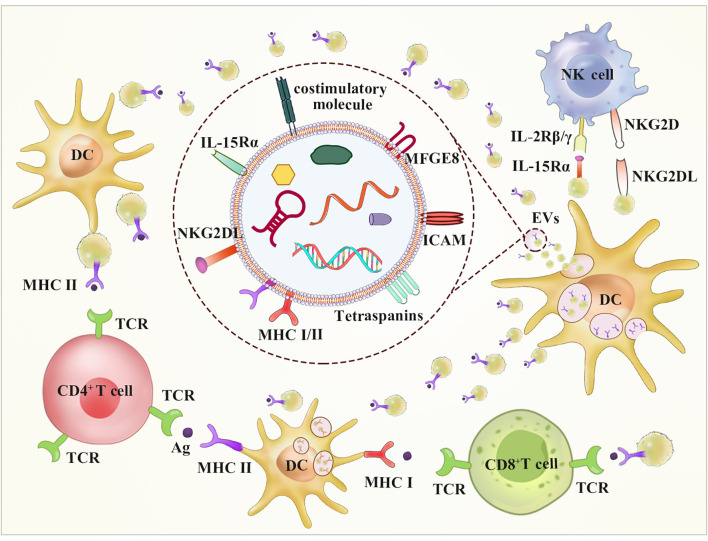
Figure 3.
DC-derived EVs may stimulate both CD8+ and CD4+ T cells by direct and indirect routes. A route for DC EVs stimulation of T cells occurs directly via the expression of MHC-I, MHC-II and costimulatory molecules on the surface of it. The indirect way stimulation of T cells occurs via bystander DCs through two mechanisms. The first way involves EVs internalization and transfer of antigen-MHC complex. The other way called cross-dressing involves antigen-MHC complex direct transfer to DC surface. Additionally, DC EVs have been shown to possess NKG2D-L and the IL-15/IL-15Rα complex, which can result in NK activation.