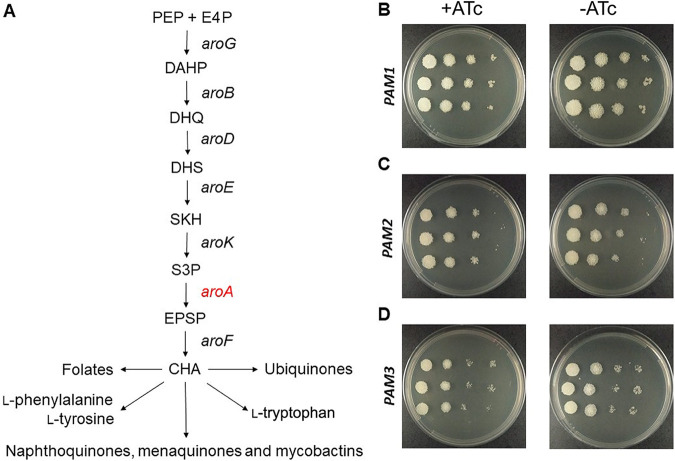
FIG 4.
Growth impairment of aroA-knockdown cells are rescued by AroAA supplementation. (A) Schematic representation of the shikimate pathway and the end products of pathways starting with chorismate. PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate; E4: d-erythrose 4-phosphate; aroG: gene encoding DAHP synthase (DAHPS); DAHP: 3-deoxy-d-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate; aroB: gene encoding DHQ synthase (DHQS); DHQ: 3-dehydroquinate; aroD: gene encoding DHQ dehydratase (DHQD); DHS: 3-dehydroshikimate; aroE: gene encoding SKH dehydrogenase (SDH); SKH: shikimate; aroK: gene encoding SKH kinase (SK); S3P: shikimate-3-phosphate; aroA: gene encoding EPSP synthase (EPSPS); EPSP: 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate; aroF: gene encoding chorismate synthase (CS); CHO: chorismate. (B to D) Dilution spots of aroA-knockdown cells (+ATc) and control cells (−ATc) grown in defined solid medium (7H10) supplemented with AroAAs (l-phenylalanine, l-tyrosine and l-tryptophan). +ATc: presence of anhydrotetracycline (100 ng/mL); −ATc: absence of anhydrotetracycline. (B) aroA-knockdown strain containing sgRNA directed to sequence adjacent to PAM1. (C) aroA-knockdown strain containing sgRNA directed to sequence adjacent to PAM2. (D) aroA-knockdown strain containing sgRNA directed to sequence adjacent to PAM3.