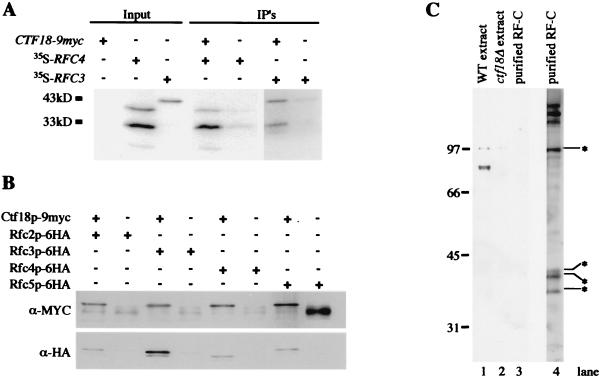
FIG. 6.
Ctf18p interacts with a subset of RF-C components but is not a component of purified RF-C. (a) Unlabeled Ctf18p-9myc was used to pull down [35S]methionine-labeled Rfc3p or Rfc4p. The slowest-migrating bands are approximately the size expected for full-length products; the faster-migrating bands are consistent with the positions of in-frame translational start sites. Similar results were obtained from four independent trials. (B) Immunoprecipitation experiments were performed in yeast whole-cell extracts from strains containing 6HA epitope-tagged alleles of Rfc2p, Rfc3p, Rfc4p, or Rfc5p in the presence and absence of a CTF18-9myc allele. Duplicate SDS-PAGE gels loaded as shown were transferred and probed with anti-myc and anti-HA antibodies. The slowest-migrating species detected by the anti-myc antibody corresponds to Ctf18p-9myc. Species detected by the α-HA antibody are consistent with the expected migrations for RF-C proteins as indicated. Note that excess immunoprecipitate was loaded in the rightmost lane, accounting for the increased intensity of the background cross-reactive band. (C) A 100-ng portion of purified RF-C complex was probed for the presence of Ctf18p using affinity-purified antibody 10C. The antibody detected a strong band at 85 kDa in protein from wild-type cells (WT extract, from YPH499) that was absent from ctf18Δ cells (ctf18Δ extract, from YE105). Lanes 1 to 3 show the Western blot, and lane 4 is silver stained SDS-PAGE. Starred species are those identified by Fien and Stillman (23) and Cullmann et al. (17).