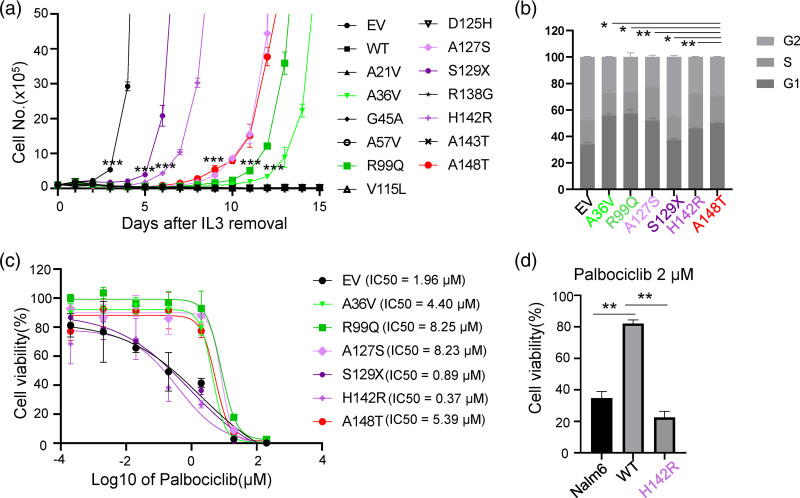
Fig. 3.
Functional characterization of p16INK4A coding variants. (a) Cytokine-independent growth of Ba/F3 cells co-expressing wildtype, variant p16INK4A, or empty vector and leukemia oncogenic BCR–ABL1 fusion gene. Cell proliferation in the absence of cytokine IL3 was measured daily as an indicator of leukemic transformation. T-test was used to compare the cell numbers of the indicated cells with Ba/F3 cells expressing wildtype p16INK4A. (b) Cell cycle analysis of transformed Ba/f3 cells, expressing indicated variant p16INK4A or empty vector. Ba/F3 cells were fixed with 66% Ethanol and then stained with propidium iodine and RNase, followed by Flow cytometric and Flowjo analysis. (c) Cytotoxicity of Palbociclib towards Ba/F3 cells. Ba/F3 cells expressing the indicated vectors were treated with increasing concentrations of Palbociclib for 48 h before assessing viability using a CCK8 assay. (d) Cytotoxicity of Palbociclib towards Nalm6 cells. Nalm6 cells expressing empty vector, p16INK4A, or p16INK4A p.H142R, were treated with 2 μM Palbociclib for 72 h and then analyzed by CCK8 assay. All experiments were repeated twice in triplicate, and data represent the mean of three replicates ± SEM. Asterisks represent statistical significance (*P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001). WT, wild type; EV, empty vector.