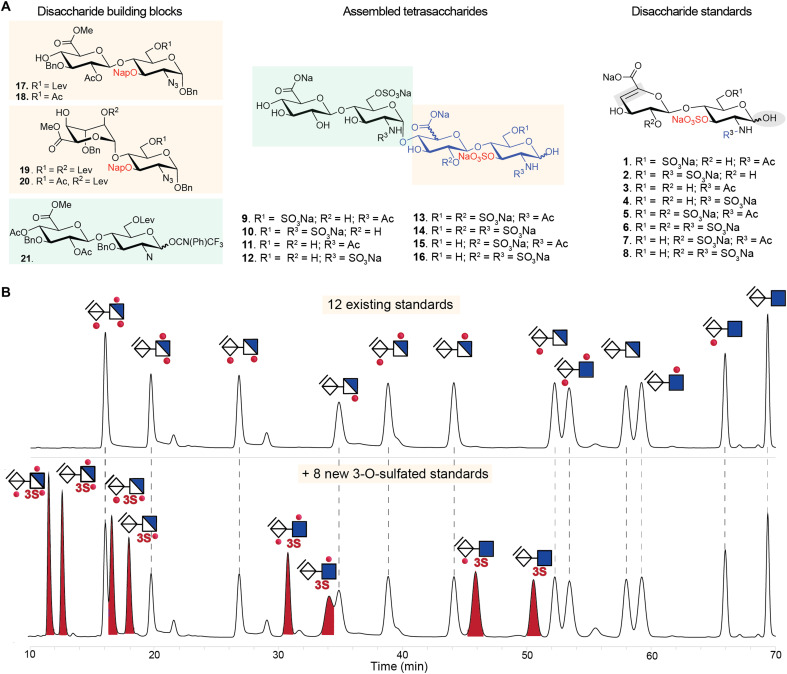
Fig. 2. Synthetic route to access 3-O-sulfated HS disaccharide standards underpinning a comprehensive HPLC-based disaccharide composition method for heparin/HS.
(A) A modular synthetic approach from common disaccharide building blocks was used to generate tetramers, followed by a sequence of O- and N-sulfation and global deprotection to yield sulfated tetrasaccharides, which, upon lyase digestion, afforded eight 3-O-sulfated authentic disaccharide standards (1 to 8 on the right of the figure). Supplementary experimental methods provide complete details of synthesis and analysis. (B) Upper chromatogram shows C18 HPLC separation of the 12 commonly used commercially available disaccharide standards, while lower chromatogram shows separation of an expanded panel of disaccharide standards including the eight 3-O-sulfated disaccharides synthesized as above in (A). AMAC-labeled disaccharides (20 pmol) were separated in each run using a gradient elution program of 0 to 18 min (18.5% buffer B), 18 to 30 min (18.5 to 19% B), 30 to 57 min (19 to 27% B), and 57 to 70 min (27 to 51% B) at 0.2 ml/min at 30°C and fluorescence detection at 525 nm. Dotted lines indicate elution times for disaccharide standards. Peaks at ~22, ~29, and ~32 min are derived from the ΔUA-GlcNS6S (D0S6), ΔUA2S-GlcNS (D2S0), and ΔUA2S-GlcNAc3S6S (D2A9) disaccharides, respectively.