Hydrogen bond and intermolecular interaction geometries (Å, °) for compounds 2 and 3a.
| D–H⋯A | D–H | H⋯A | D⋯A | ∠D–H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | ||||
| N003–H003⋯N004i | 0.83 (2) | 2.18 (2) | 3.007 (2) | 176 (2) |
| C007–H007⋯O002ii | 1.00 (2) | 2.41 (2) | 3.388 | 165 |
| 3 | ||||
| O1–H1B⋯O004 | 0.850 | 1.9771 | 2.773 (7) | 155.4 |
| N00B–H00B⋯O004 | 0.84 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.832 (1) | 173 (2) |
| N00C–H00C⋯O003 | 0.85 (2) | 2.09 (2) | 2.932 (1) | 169 (2) |
| N00D–H00D⋯N006i | 0.88 (2) | 2.17 (2) | 3.043 (1) | 173 (2) |
| N008–H008⋯N005i | 0.88 (2) | 2.10 (2) | 2.953 (1) | 162 (1) |
| N00A–H00A⋯N007i | 0.87 (2) | 2.15 (2) | 2.995 (1) | 163 (2) |
| N009–H009⋯N00Ei | 0.82 (2) | 2.13 (2) | 2.938 (1) | 173 (2) |
| C00U–H00U⋯N00Fii | 0.950 | 2.527 | 3.318 (2) | 140.72 |
| C012–H012⋯C00Mii | 0.950 | 2.822 | 3.542 (2) | 133.38 |
| C014–H014⋯O1iii | 0.950 | 2.532 | 3.352 (8) | 144.5 |
| π⋯π* | — | — | 3.678 | — |
Symmetry transformations used to generate equivalent atoms for 2: (i) 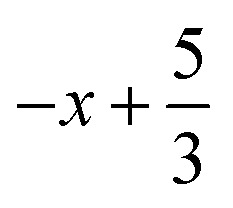 ,
, 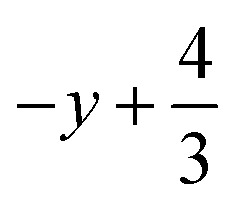 ,
, 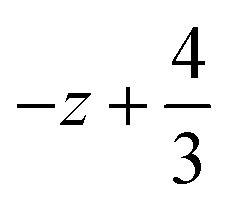 ; (ii)
; (ii) 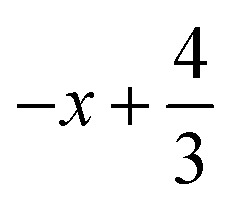 ,
, 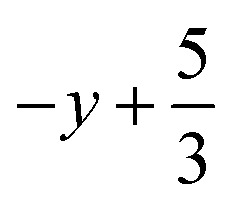 ,
, 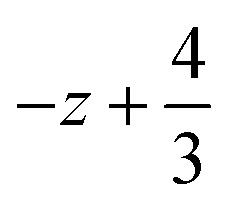 ; for 3: (i)
; for 3: (i) 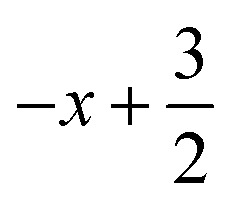 ,
, 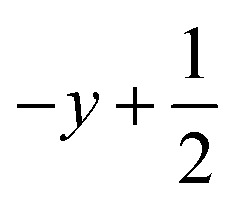 ,
, 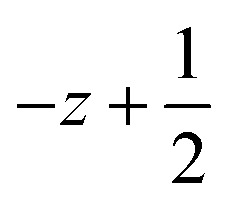 ; (ii)
; (ii) 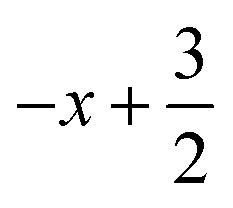 ,
, 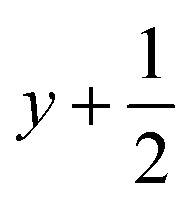 ,
, 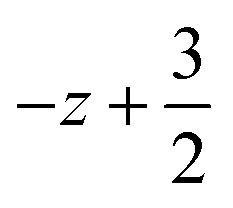 ; (iii) −x, −y +1, −z +1; *For π⋯π interactions d(D⋯A) = Cg⋯Cg and for C–H⋯π interactions d(H⋯A) = H⋯Cg, where Cg = centroid of the aromatic pyridine rings.
; (iii) −x, −y +1, −z +1; *For π⋯π interactions d(D⋯A) = Cg⋯Cg and for C–H⋯π interactions d(H⋯A) = H⋯Cg, where Cg = centroid of the aromatic pyridine rings.
