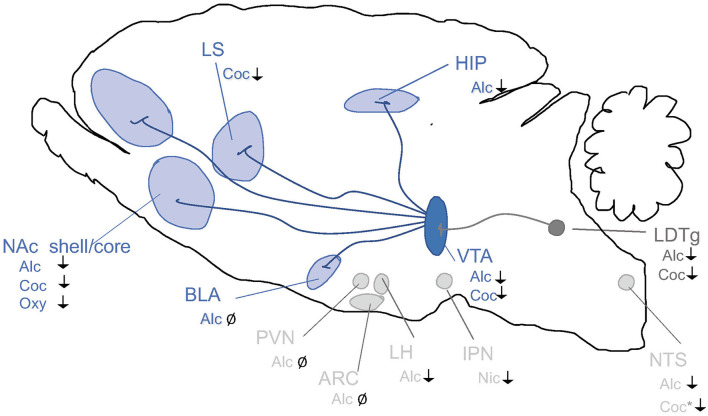
Figure 4.
Schematic illustrations of brain regions important for the interaction between the GLP-1 pathway and addiction processes. GLP-1R agonists attenuate behaviors relating to reward and intake of alcohol (Alc), nicotine (Nic), cocaine (Coc) and oxycodone (Oxy). Nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) of the brain stem, ventral tegmental area (VTA), nucleus accumbens (NAc) shell, laterodorsal tegmental area (LDTg), basolateral amygdala (BLA), lateral septum (LS) and hippocampus (HIP), paraventricular nucleus (PVN), arcuate nucleus (ARC) and lateral hypothalamus (LH) and interpeduncular nucleus (IPN). ↓ Shows an attenuation and Ø reflects no change. *Role shown indirectly.