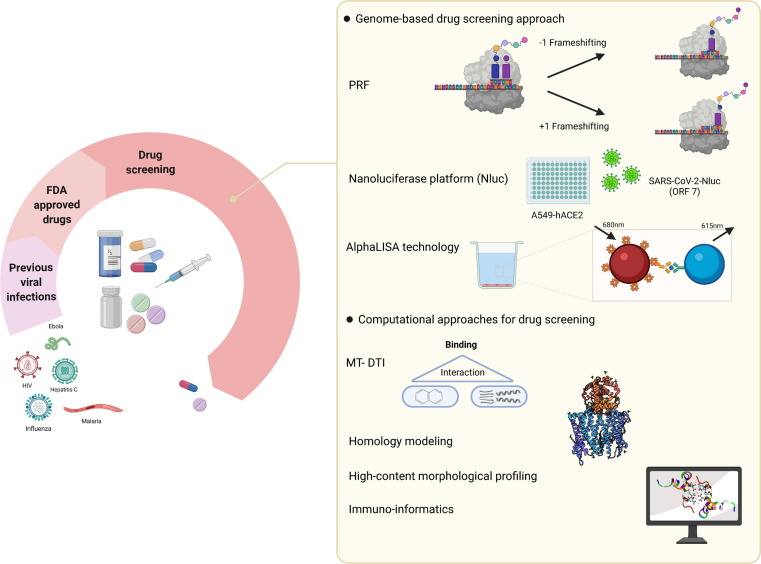
Figure 3.
Drug-screening platforms. Genome-based strategies and computational approach are two main measures for drug-screening against coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19). Using programmed ribosomal frameshifting (PRF), a strategy for the translation of nonstructural viral proteins, the efficacy of many US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs have been evaluated in the context of COVID-19. Another genome-based strategy, Nluc, is taking advantage of nanoluciferase gene insertion in viral genome and provides both diagnostic and therapeutic applications for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). In AlphaLISA technology, excitation of the donor bead at a certain wavelength leads to generation of radical oxygen species, which activates the acceptor bead to produce light. Computational approaches comprise MT-DTI, homology modeling, high-content morphological profiling, and immunoinformatics. The first three strategies have been used so far to evaluate a range of FDA-approved drugs against SARS-CoV-2, whereas immunoinformatics is applied for the detection of the most reliable antigens able to confer the ability to produce strong immune responses and can be used in vaccine development. Abbreviation: AlphaLISA, amplified luminescent proximity homogenous assay.