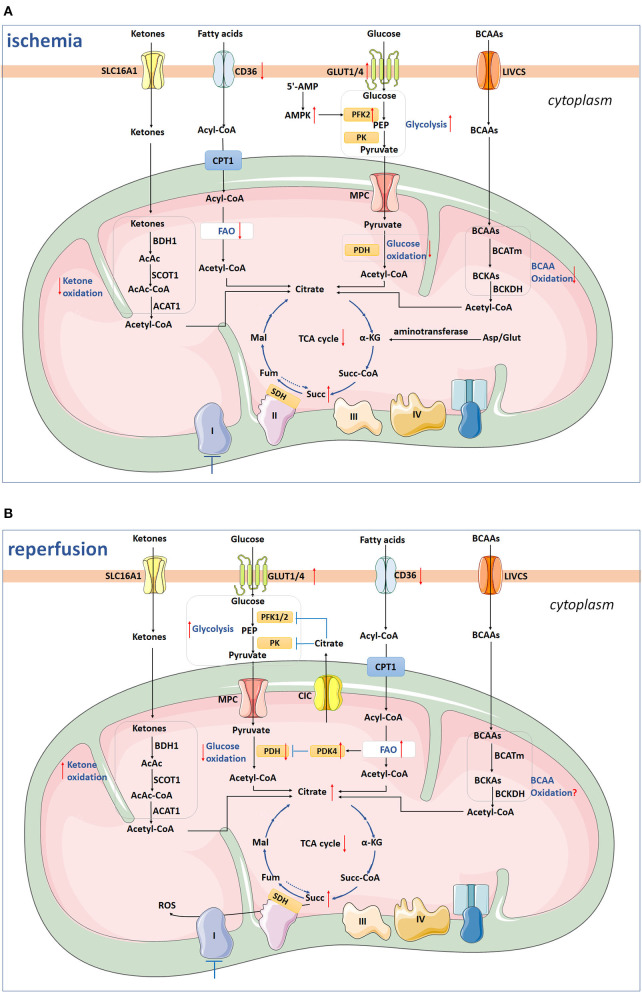
Figure 1.
The scheme depicts ketone oxidation, glycolysis, glucose oxidation, fatty acid oxidation, BCAA oxidation, and succinate metabolism under ischemia (A) and reperfusion (B). (A) Under ischemia, GLUT4-mediated glucose uptake and glycolysis are increased by AMPK-induced PFK-2 activation, whereas glucose oxidation is shuttled down. The CD36 on sarcolemma, FAs uptake, and FAO are inhibited. Besides, BCAAs and ketones oxidation are also inhibited during ischemia. The TCA cycle and Complex I are inhibited, while the succinate is accumulated from existing metabolites of TCA with mitochondrial Complex II reversal and aminotransferase anaplerosis. (B) During reperfusion, CD36 remains low, while FAO returns to the pre-ischemic level. High levels of NADH, acetyl-CoA, and ATP in mitochondria generated from increased FAO inhibit activated PDH via activating PDK4 and, therefore, inhibit glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation. The glycolysis still remains high, while glucose oxidation is inhibited. Ketones utilization is increased, while the level of BCAAs oxidation remains to be clarified in the future. Two-thirds of succinate enters into perfusate, and the remaining one-third of succinate is oxidized via SDH, driving ROS burst. SLC16A1, Solute carrier (SLC) 16A1/monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1); β-OHB, β-hydroxybutyrate; AcAc, acetoacetate; BDH1, β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase 1; SCOT, succinyl-CoA:3 oxoacid-CoA transferase; AcAc-CoA, catalyze acetoacetyl-CoA; ACAT1, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 1; CPT1, carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1; FAO, fatty acids oxidation; GLUT1/4, glucose transporter 1/4; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PK, pyruvate kinase; MPC, mitochondrial pyruvate carrier; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; BCAAs, branched chain amino acids; LIVCS, Leu, Ile, Val: cation symporter; BCKAs, α-keto-acids; BCATm, mitochondrial branched chain aminotransaminase; BCKDH, branched chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; Fum, fumarate; Mal, malate; Succ, succinate; Succ-CoA, succinyl-CoA; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; Asp, aspartate; Glut, glutamine. The arrow facing up represents an increase, and down indicates a decrease. Blue lines with a T shape represent inhibition.