Figure 2.
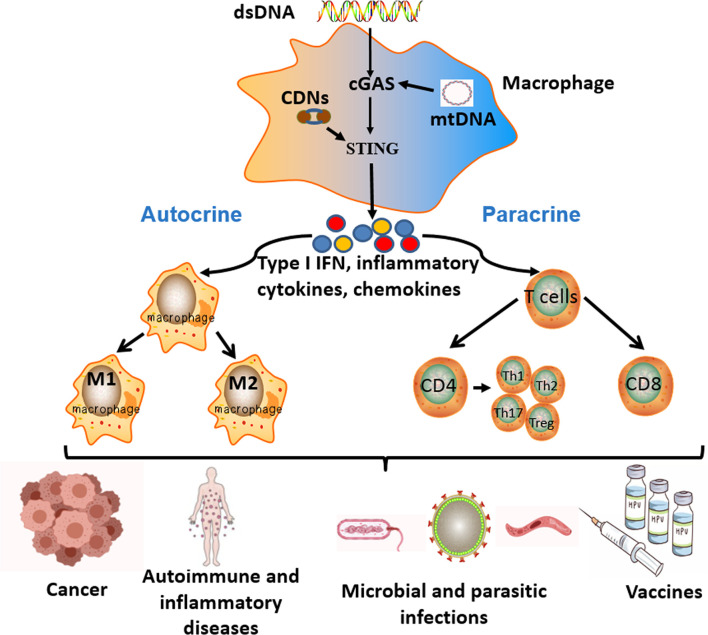
The key roles and effects of the cGAS-STING signal pathway in different diseases. Free cytoplasmic dsDNA or CDNs could activate the cGAS-STING signal pathway of antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Activation of the cGAS-STING signal pathway induces a series of immune cascades to produce diverse products, including type I IFN, inflammatory cytokines, and chemokines. These products have significant influences on the host immune microenvironment in both autocrine and paracrine ways. In an autocrine way, it could promote the maturation, activation, and polarization of macrophages. In a paracrine way, the different cytokines produced by APCs could recruit T lymphocytes and promote their proliferation and differentiation. All the above immune responses participate in the pathogenesis and progression of various diseases, as well as the effective process of vaccines.