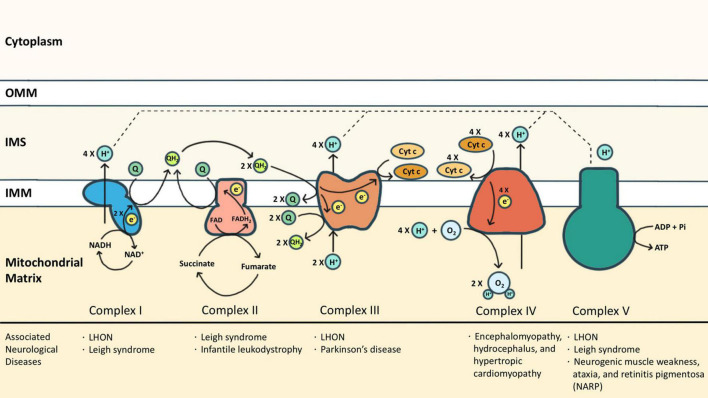
FIGURE 1.
The electron transport chain (ETC) consists of complexes I (cI) to V (cV), as well as two free electron carriers, CoQ and cyt c. NADH and FADH2 donated electrons to cI and cII, respectively, causing reduction of CoQ into CoQH2. The CoQH2 is in turn oxidized by cIII where the electrons are delivered to cyt c. The reduced cyt c was then oxidized by cIV where the oxygen molecule was reduced as the terminal electron acceptor. Protons accumulated in the intermembrane space during oxidative phosphorylation via cI, cIII, and cIV, and are essential for cV to drive ATP synthesis. Some neurological diseases associated with mutations of cI-cV are listed.