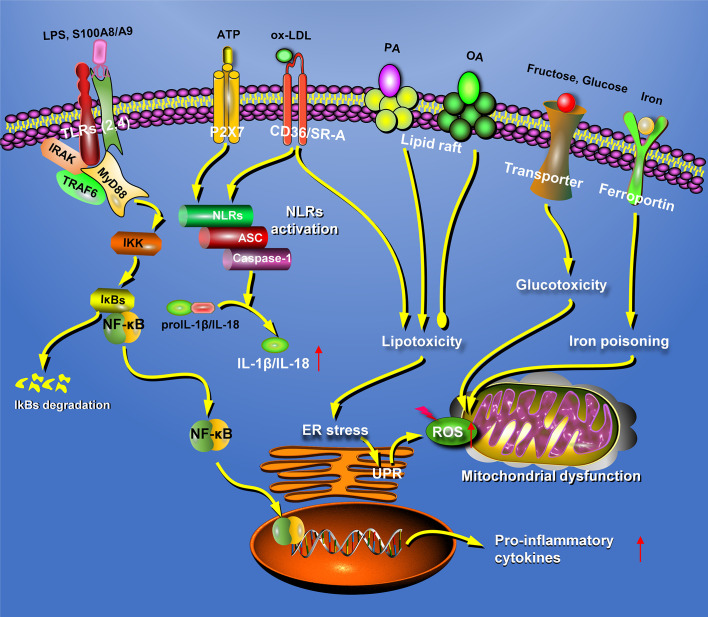
Figure 2.
Hepatic macrophages participate in the pathogenesis of fatty liver disease in many different patterns. In fatty liver disease, the macrophages can recognize extracellular stimuli through pattern recognition receptors, including TLRs and NLRs, resulting in the secretion of inflammatory factors. In addition, macrophages could also participate in the progression of NAFLD through lipotoxicity, glucotoxicity, and iron poisoning. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; NLRs, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors; OA, oleic acid; PA, palmitic acid; P2X7, P2X purinoceptor 7; ROS, reactive oxygen species; S100A8, S100 calcium-binding proteins A8; SR-A, scavenger receptor-A; TLRs, Toll-like receptors; UPR, unfolded protein response.