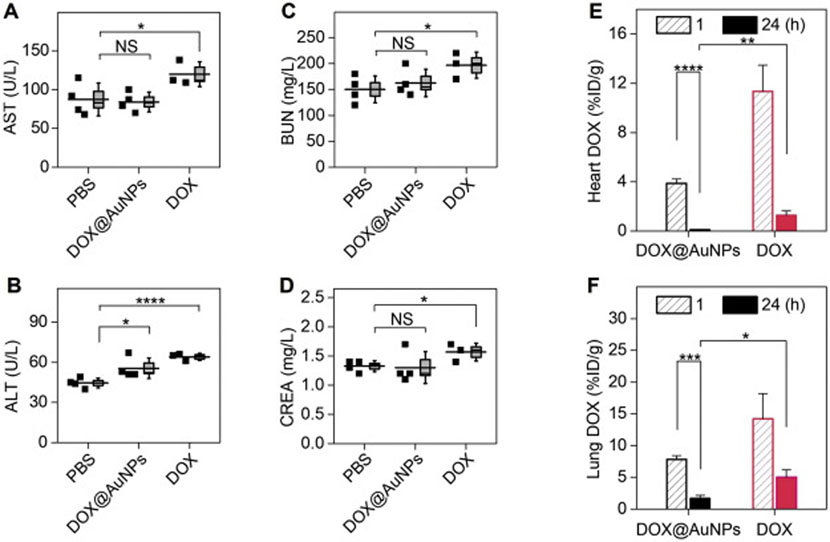
Fig. 9.
Minimized toxicity of loaded drug (DOX) using renal clearable nanocarriers. (A-D) Blood chemistry analysis after successive treatments, suggesting the renal clearable DDS (DOX@AuNPs) can minimize the impairment of DOX to liver and kidney functions. Aspartate transaminase, AST (A), alanine aminotransferase, ALT (B), blood urea nitrogen, BUN (C), creatinine, CREA (D). *P < .05, ****P < .0001, NS, not significant (n = 4 for DOX@AuNPs and PBS; n = 3 for free DOX, where one animal died during study). (E-F) DOX biodistribution study, showing renal clearable nanocarriers can significantly minimize the drug accumulation and retention in vital organs, including heart (E) and lungs (G) (n = 3). *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .005, ****P < .0001 (Student’s t-test). Adapted from ref. [151].