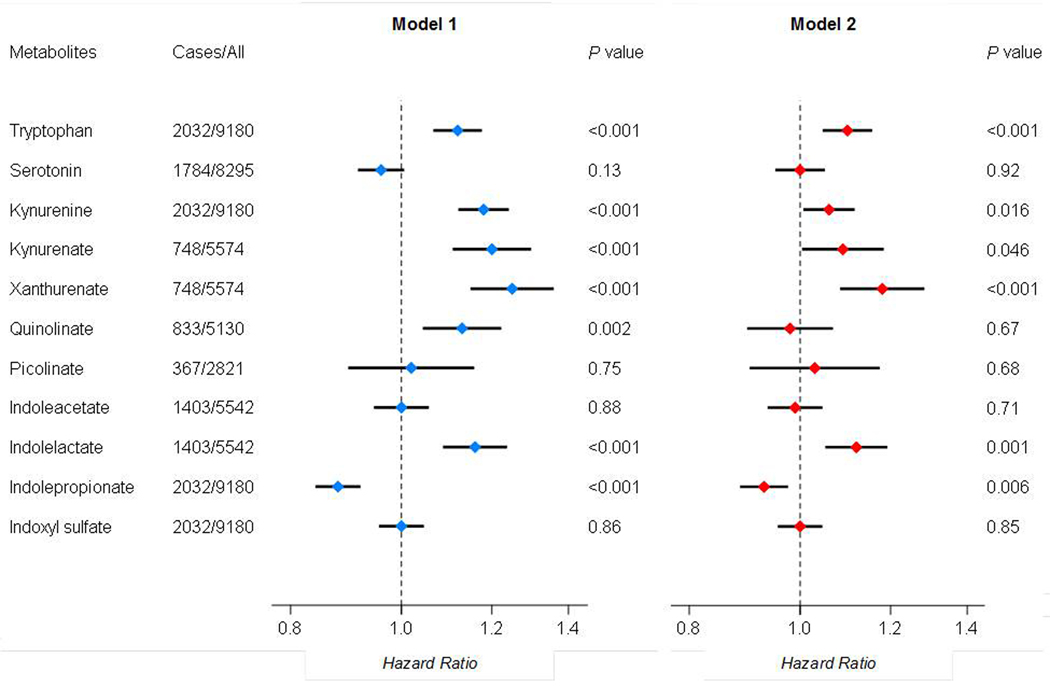
Figure 2. Associations between circulating tryptophan metabolite levels and incident type 2 diabetes.
Data are Hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals of incident type 2 diabetes per standard deviation increment in metabolite levels, adjusted for age, sex, smoking, alcohol consumption, education, family income, family history of diabetes, self-reported hypertension and/or antihypertensive medication use, self-reported dyslipidemia and/or lipid-lowering medication us, and other study-specific covariates (Model1); and further adjusted for body mass index and waist-to-hip ratio (Model 2). Results across 5 studies were combined by fixed-effect meta-analysis.