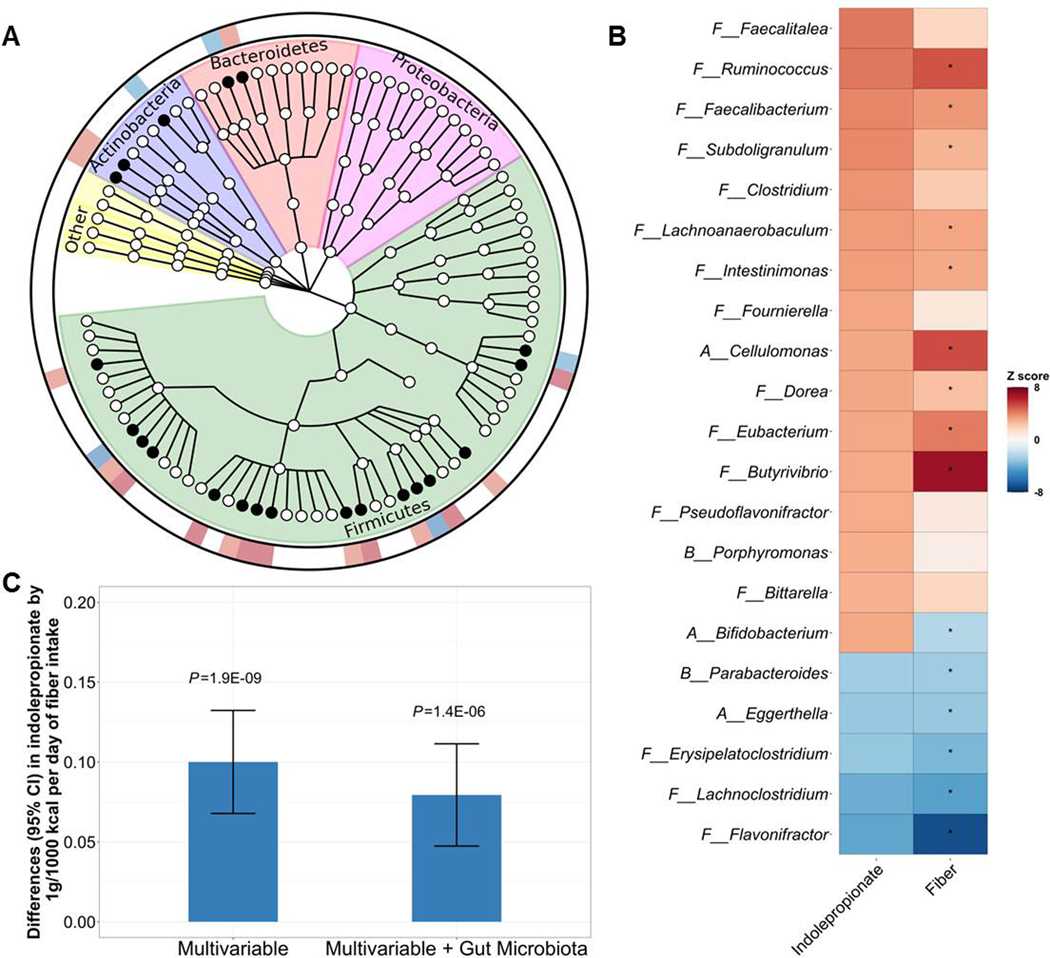
Figure 5. Dietary fiber intake, gut microbiota and serum indolepropionate.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of taxonomic features in association with host serum indolepropionate levels in the HCHS/SOL. A total of 21 gut microbial genera significantly associated with serum indolepropionate (FDR<0.05) are indicated by solid circles. Data showing in the outer ring are effect sizes (positive, red; inverse, blue) of gut microbiota genera on serum indolepropionate. (B) Associations of 21 indolepropionate-assocaited gut microbial genera with dietary fiber intake in the HCHS/SOL. To show comparable estimates for the associations of gut microbial genera with indolepropionate and fiber intake, data are presented as Z-scores (regression coefficients/standard errors). *FDR<0.05 for the associations between dietary fiber intake and gut microbial genera. (C) Associations between dietary fiber intake and serum indolepropionate levels with and without adjustment for gut microbiota (20 indolepropionate-associated gut microbial genera) in the HCHS/SOL. Bifidobacterium, which showed opposite associations with indolepropionate and fiber intake, was not included.